Fichier:Effet de Serre.png
Fichier d’origine (794 × 611 pixels, taille du fichier : 73 Kio, type MIME : image/png)
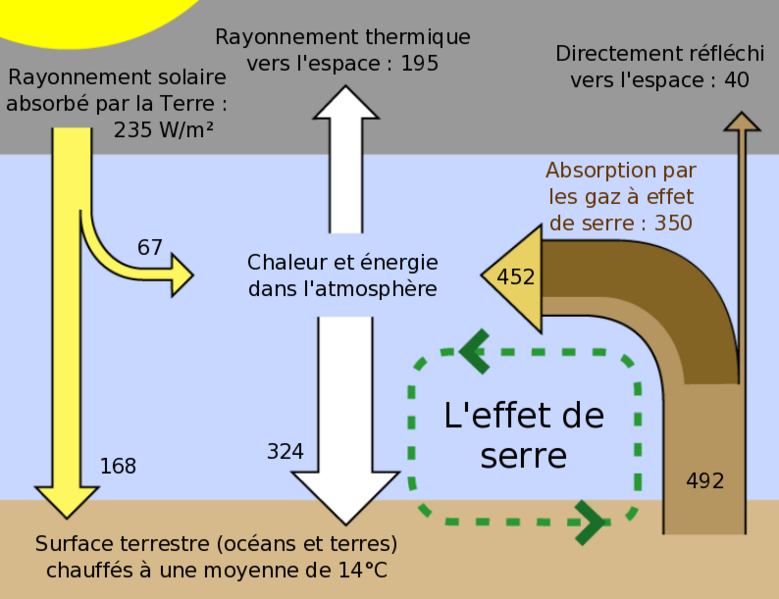
This figure is a simplified, schematic representation of the flows of energy between space, the atmosphere, and the Earth's surface, and shows how these flows combine to trap heat near the surface and create the greenhouse effect. Energy exchanges are expressed in watts per square meter (W/m2) and derived from Kiehl & Trenberth (1997).
The sun is ultimately responsible for virtually all energy that reaches the Earth's surface. Direct overhead sunlight at the top of the atmosphere provides 1366 W/m2; however, geometric effects and reflective surfaces limit the light which is absorbed at the typical location to an annual average of ~235 W/m2. If this were the total heat received at the surface, then, neglecting changes in albedo, the Earth's surface would be expected to have an average temperature of -18 °C (Lashof 1989). Instead, the Earth's atmosphere recycles heat coming from the surface and delivers an additional 324 W/m2, which results in an average surface temperature of roughly +14 °C [1].
Of the surface heat captured by the atmosphere, more than 75% can be attributed to the action of greenhouse gases that absorb thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface. The atmosphere in turn transfers the energy it receives both into space (38%) and back to the Earth's surface (62%), where the amount transferred in each direction depends on the thermal and density structure of the atmosphere.
This process by which energy is recycled in the atmosphere to warm the Earth's surface is known as the greenhouse effect and is an essential piece of Earth's climate. Under stable conditions, the total amount of energy entering the system from solar radiation will exactly balance the amount being radiated into space, thus allowing the Earth maintain a constant average temperature over time. However, recent measurements indicate that the Earth is presently absorbing 0.85 ± 0.15 W/m2 more than it emits into space (Hansen et al. 2005). This increase, associated with global warming, is believed to have been caused by the recent increase in greenhouse gas concentrations.
Historique du fichier
Cliquer sur une date et heure pour voir le fichier tel qu'il était à ce moment-là.
| Date et heure | Vignette | Dimensions | Utilisateur | Commentaire | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| actuel | 28 novembre 2008 à 13:13 |  | 794 × 611 (73 Kio) | Admin (discussion | contributions) | This figure is a simplified, schematic representation of the flows of energy between space, the atmosphere, and the Earth's surface, and shows how these flows combine to trap heat near the surface and create the greenhouse effect. Energy exchanges are exp |
Vous ne pouvez pas remplacer ce fichier.
Utilisation du fichier
Le fichier suivant est un doublon de celui-ci (plus de détails) :
- Fichier:Effet de Serre.png de : Wikimedia Commons
La page suivante utilise ce fichier :