Différences entre versions de « Didactics »
| Ligne 1 : | Ligne 1 : | ||
{{Widget:Fiche-Conceptuelle-Haut}} | {{Widget:Fiche-Conceptuelle-Haut}} | ||
| − | = {{Widget: | + | = {{Widget:Traduction-Fiche}} = |
<!-- ***********************************************************************--> | <!-- ***********************************************************************--> | ||
Version du 30 mai 2023 à 12:05
 Traduction
Traduction
 Définition
Définition
Domaine, Discipline, Thématique
Définition écrite
- Didactics is the art of teaching. It’s the study of how to teach, and it’s also the philosophy of education. It focuses on four main areas: learning, teaching, research and evaluation.
In addition, it can be divided into two categories: theoretical and practical didactics.
Theoretical didactics are used to study how people learn, and how they can be taught more effectively, while practical didactics focus on teaching methods based on this research.
- Didactics can also be defined as the science of teaching and learning. She is interested in how knowledge, skills and values are transmitted and acquired, and the methods, tools and techniques that facilitate this process.
Didactics is therefore concerned with all aspects of teaching, from the planning of courses to the implementation of pedagogical activities, including the evaluation of learning. It takes into account the characteristics of learners (age, level, learning style, etc.) and the constraints of the educational context (curriculum, resources, etc.).
Didactics can be applied to all areas of knowledge and all levels of education, from kindergarten to university to vocational training. It draws on research in educational sciences, learning psychology, educational sociology, disciplinary didactics, etc. to develop effective pedagogical approaches adapted to the needs of learners.
....................................................................... ....................................................................... .......................................................................
....................................................................... ....................................................................... |
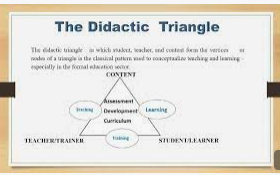
Définition graphique
 Concepts ou notions associés
Concepts ou notions associés
 Exemples, applications, utilisations
Exemples, applications, utilisations
|
 Erreurs ou confusions éventuelles
Erreurs ou confusions éventuelles
- .........................................
- .........................................
![]() Confusion possible ou glissement de sens
Confusion possible ou glissement de sens
- Confusion entre conceptions - representation
- Confusion entre Didactics - pedagogy
- ....................
 Questions possibles
Questions possibles
- What is the role of didactics in education?
- How does didactics contribute to effective teaching and learning?
- What are the key principles and theories of didactics?
- How can didactics inform instructional design and lesson planning?
- What strategies and methods can be employed in didactics to enhance student engagement and understanding?
- How does didactics address the diverse needs and learning styles of students?
- What is the relationship between didactics and curriculum development?
- How can technology be integrated into didactics to support teaching and learning?
- What are some effective assessment strategies within the framework of didactics?
- How can didactics be used to promote critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity in students?
 Liaisons enseignements et programmes
Liaisons enseignements et programmes
Idées ou Réflexions liées à son enseignement
- Student-Centered Approach: Embrace a student-centered approach where the focus is on the needs, interests, and active engagement of students. Design lessons that encourage student participation, foster inquiry and critical thinking, and provide opportunities for collaboration and problem-solving.
- Differentiated Instruction: Recognize and accommodate the diverse learning needs of students by applying differentiated instruction strategies. Tailor instruction to address individual strengths, interests, and learning styles, and provide appropriate support and challenges to maximize student growth.
- Active Learning: Promote active learning by incorporating hands-on activities, discussions, debates, and practical applications of knowledge. Encourage students to construct their understanding through exploration, experimentation, and reflection.
- Formative Assessment: Implement ongoing formative assessment practices to monitor student progress, identify misconceptions, and provide timely feedback. Use a variety of assessment methods, such as class discussions, quizzes, and observations, to inform instructional decisions and support student learning.
- Cultivate a Positive Learning Environment: Foster a positive and inclusive learning environment where students feel safe, respected, and supported. Build strong teacher-student relationships, encourage peer collaboration, and create opportunities for open dialogue and active participation.
- Incorporate Technology: Integrate educational technologies thoughtfully to enhance teaching and learning experiences. Use digital tools, multimedia resources, and online platforms to facilitate interactive learning, promote information access and sharing, and develop digital literacy skills.
- Reflective Practice: Engage in reflective practice to continually improve teaching approaches. Regularly reflect on lesson outcomes, student feedback, and personal teaching experiences. Adapt teaching strategies based on insights gained from self-reflection and professional development opportunities.
- Collaboration and Professional Growth: Seek opportunities for collaboration with colleagues, participate in professional learning communities, and engage in continuous professional development. Share ideas, exchange best practices, and stay updated on current research and advancements in the field of education.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Be flexible and adaptable in response to the dynamic nature of teaching and the evolving needs of students. Adjust instructional strategies, approaches, and resources based on student feedback, emerging trends, and individual student progress.
- Cultivate a Love for Lifelong Learning: Instill a love for lifelong learning in students by modeling enthusiasm, curiosity, and a growth mindset. Encourage students to take ownership of their learning, set goals, and develop the skills and habits necessary for lifelong learning and success.
Aides et astuces
Education: Autres liens, sites ou portails
 Bibliographie
Bibliographie
Pour citer cette page: ([1])
ABROUGUI, M & al, 2023. Didactics. In Didaquest [en ligne]. <http:www.didaquest.org/wiki/Didactics>, consulté le 24, novembre, 2024
- ..................
- ..................
- ..................
- ..................
- Sponsors Education
- Didactics and Pedagogy (Concepts)
- Didactics and Constructivism (Concepts)
- The Didactic Triangle (Concepts)
- Didactic Transposition (Concepts)
- Conceptions and Representations (Concepts)
- Didactic Obstacles (Concepts)
- The Didactic Contract (Concepts)
- Perverse Effects of the Didactic Contract (Concepts)
- Teaching and Learning
- Curriculum
- Instructional Design
- Pedagogical Approaches
- Assessment
- Differentiation
- Motivation
- Learning Environment
- Teacher-Student Interaction
- Reflective Practice
- Concepts
- Didactics
- Didactics (Concepts)
- Fiche conceptuelle didactique