Différences entre versions de « ICT and ineractive learning »
| Ligne 201 : | Ligne 201 : | ||
How: Discussions provide a platform for students to share ideas, ask questions, and engage in meaningful conversations outside the classroom, promoting collaborative learning. | How: Discussions provide a platform for students to share ideas, ask questions, and engage in meaningful conversations outside the classroom, promoting collaborative learning. | ||
}}<!--************** Fin Fiche Didactique Explicitations ******************* --> | }}<!--************** Fin Fiche Didactique Explicitations ******************* --> | ||
| + | |||
= {{Widget:Erreurs-confusions-Fiche}} = | = {{Widget:Erreurs-confusions-Fiche}} = | ||
| Ligne 213 : | Ligne 214 : | ||
{{@}} '''Erreur: Croire que''' | {{@}} '''Erreur: Croire que''' | ||
| − | * | + | * ICT tools are always used to facilitate interactive learning experiences. |
| − | * | + | * Interactive whiteboards and educational apps are the only way to create interactive lessons that cater to different learning styles |
{{@}} '''Confusion possible ou glissement de sens''' | {{@}} '''Confusion possible ou glissement de sens''' | ||
| − | * Confusion entre [[ | + | * Confusion entre [[ICT - Interactive learning]] |
| − | * Confusion entre [[ | + | * Confusion entre [[Perception of ICT as a Tool - Pedagogical Approach]] |
{{@}} '''Erreur fréquente''': | {{@}} '''Erreur fréquente''': | ||
| − | * ... | + | * Assuming that using ICT in the classroom means simply replacing traditional teaching methods with digital tools without fundamentally changing the approach to instruction. |
| + | * Focusing solely on the technology aspect (hardware and software) without considering how it enhances interactivity and learning outcomes. | ||
| + | * Assuming that using the latest technology automatically improves learning outcomes, neglecting the importance of pedagogical strategies and instructional design | ||
| + | * Neglecting the importance of student engagement and active participation in the learning process. | ||
| + | |||
}}<!-- ************** Fin Fiche Didactique Conceptions ********************* --> | }}<!-- ************** Fin Fiche Didactique Conceptions ********************* --> | ||
Version du 26 novembre 2023 à 14:26
 Traduction
Traduction
[[{TIC et apprentissage interactif}}]] (Français)
/ ICTs and interactive learning (Anglais)
/ تكنولوجيا المعلومات و التعلم التفاعلي (Arabe)
Définition =
Domaine, Discipline, Thématique
Définition écrite
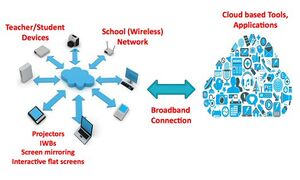
ICT, or Information and Communication Technology, refers to a set of tools and technologies used for collecting, processing, storing, transmitting, and presenting information. When combined with interactive learning, it becomes a set of technological resources and devices used to create dynamic and engaging learning environments. Interactive learning emphasizes the active involvement of learners in the knowledge acquisition process. It uses ICT to encourage learner participation, collaboration, and feedback, thereby promoting deeper understanding and knowledge retention. This learning approach can take various forms, such as simulations, online discussions, problem-solving exercises, interactive quizzes, and multimedia resources, contributing to a more enriching and interactive educational experience
https://youtu.be/oOBnZpeurT8?si=5lPGecVvtFzaGnMj
|
[[]]
Définition graphique
- AUTRES MEDIAS
![]() and ineractive learning ICT and ineractive learning
and ineractive learning ICT and ineractive learning
![]() and ineractive learning ICT and ineractive learning
and ineractive learning ICT and ineractive learning
![]() Représentation graphique spatiale ICT and ineractive learning
Représentation graphique spatiale ICT and ineractive learning
 Concepts ou notions associés
Concepts ou notions associés
| Blended Learning | E-Learning | Flipped Classroom | Assessment for Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| A combination of traditional face-to-face instruction and online learning, often using ICT. | Learning conducted via electronic media, typically on the internet. | Inverts the traditional teaching model by delivering instructional content online outside of class and using class time for interactive activities. | Formative assessment techniques that provide ongoing feedback to students and inform instruction. |
 Exemples, applications, utilisations
Exemples, applications, utilisations
Example: Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), Microsoft Teams, or other cloud-based collaboration tools. How: These platforms allow students and teachers to collaborate on documents, presentations, and projects in real-time, promoting interactive group work and communication.
Example: Learning Management Systems (LMS) like Moodle, Canvas, or Blackboard. How: LMS platforms provide a centralized space for course materials, discussions, quizzes, and assignments, fostering interactive learning and communication between students and teachers.
How: Teachers can use interactive whiteboards to create engaging multimedia presentations, draw diagrams in real-time, and involve students in interactive activities during lessons.
Example: Kahoot!, Quizizz, or educational apps for subjects like mathematics, science, and language learning. How: Gamified apps and educational games make learning enjoyable and interactive, allowing students to test their knowledge in a fun and engaging way
Example: Zoom, Microsoft Teams, or Google Meet. How: Virtual classes enable real-time interaction between students and teachers, facilitating discussions, live demonstrations, and collaborative activities even when participants are in different locations
Example: PhET Interactive Simulations, virtual chemistry labs, or physics simulations. How: Simulations provide hands-on experiences in subjects like science and mathematics, allowing students to explore concepts in a safe and interactive virtual environment
How: Listening to podcasts or watching educational videos can be interactive by incorporating discussions, reflections, and follow-up activities related to the content.
Example: AR apps for exploring historical sites or VR simulations for virtual field trips. How: AR and VR technologies provide immersive experiences, allowing students to explore subjects like history, geography, and science in a more interactive and engaging manner.
Example: Creating digital stories using tools like Storybird, Adobe Spark, or Book Creator. How: Students can use multimedia elements to express themselves creatively, share their understanding of concepts, and collaborate on storytelling projects
Example: Discussion boards within an LMS or dedicated online forums. How: Discussions provide a platform for students to share ideas, ask questions, and engage in meaningful conversations outside the classroom, promoting collaborative learning. |
 Erreurs ou confusions éventuelles
Erreurs ou confusions éventuelles
- ICT tools are always used to facilitate interactive learning experiences.
- Interactive whiteboards and educational apps are the only way to create interactive lessons that cater to different learning styles
![]() Confusion possible ou glissement de sens
Confusion possible ou glissement de sens
- Confusion entre ICT - Interactive learning
- Confusion entre Perception of ICT as a Tool - Pedagogical Approach
- Assuming that using ICT in the classroom means simply replacing traditional teaching methods with digital tools without fundamentally changing the approach to instruction.
- Focusing solely on the technology aspect (hardware and software) without considering how it enhances interactivity and learning outcomes.
- Assuming that using the latest technology automatically improves learning outcomes, neglecting the importance of pedagogical strategies and instructional design
- Neglecting the importance of student engagement and active participation in the learning process.
 Questions possibles
Questions possibles
 Liaisons enseignements et programmes
Liaisons enseignements et programmes
Idées ou Réflexions liées à son enseignement
Aides et astuces
Education: Autres liens, sites ou portails
 Bibliographie
Bibliographie
Pour citer cette page: (and ineractive learning)
ABROUGUI, M & al, 2023. ICT and ineractive learning. In Didaquest [en ligne]. <http:www.didaquest.org/wiki/ICT_and_ineractive_learning>, consulté le 24, novembre, 2024
- ..................
- ..................
- ..................
- ..................
- Sponsors Education
- Time Managemen (Concepts)
- Focus and Attention (Concepts)
- Self-Regulation (Concepts)
- Responsible Use of Technology (Concepts)
- Digital Citizenship (Concepts)
- Cybersecurity (Concepts)
- Organizational Skills (Concepts)
- Balance (Concepts)
- Adaptability (Concepts)
- Communication (Concepts)
- Critical Thinking (Concepts)
- Digital Literacy (Concepts)
- Blended Learning
- E-Learning
- Synchronous Learning
- Asynchronous Learning
- Gamification
- Flipped Classroom
- Adaptive Learning
- Learning Management System (LMS)
- Online Collaboration Tools
- Digital Literacy
- Remote Teaching and Learning
- Peer Assessment
- Flipped Learning
- EdTech
- Concepts
- ICT and ineractive learning
- ICT and ineractive learning (Concepts)
- Fiche conceptuelle didactique