Différences entre versions de « Visual Basic .NET »
| Ligne 1 156 : | Ligne 1 156 : | ||
=== Généralités sur les contrôles === | === Généralités sur les contrôles === | ||
==== Contrôles standards ==== | ==== Contrôles standards ==== | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: justify;"><span style="font-size: medium;">La partie visuelle du projet est composée principalement d'un ou de plusieurs formulaires (Forms). Un formulaire représente une fenêtre (Window). Dans ce formulaire, on va ajouter les éléments graphiques dont on a besoin. </span></p> | ||
| + | <table class="TableGrid" style="width: 0px; border-collapse: collapse; mso-yfti-tbllook: 1184; mso-padding-alt: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt;" border="0" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0"> | ||
| + | <tbody> | ||
| + | <tr style="mso-yfti-irow: 0; mso-yfti-firstrow: yes; height: 29.3pt;"> | ||
| + | <td width="214" style="width: 160.7pt; border: solid black 1.0pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 29.3pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="center" class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 8.2pt; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 0cm; text-align: center; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="font-size: medium;"><b style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Nom de l'élément</span></b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"><o:p></o:p></span></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td width="406" style="width: 304.75pt; border: solid black 1.0pt; border-left: none; mso-border-left-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 29.3pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="center" class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 32.15pt; text-align: center; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="font-size: medium;"><b style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Utilité</span></b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"><o:p></o:p></span></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr style="mso-yfti-irow: 1; height: 29.25pt;"> | ||
| + | <td width="214" valign="top" style="width: 160.7pt; border: solid black 1.0pt; border-top: none; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 29.25pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 3.05pt; margin-bottom: 5.6pt; margin-left: 0cm; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="font-size: small;"><span class="SpellE"><b style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Form</span></b></span><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-fareast-font-family: Calibri; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"></span><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"> (feuille) <o:p></o:p></span></span></p> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 14.25pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="line-height: 107%; font-size: small; mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"><span style="mso-spacerun: yes;"> </span><o:p></o:p></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td width="406" valign="top" style="width: 304.75pt; border-top: none; border-left: none; border-bottom: solid black 1.0pt; border-right: solid black 1.0pt; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-left-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 29.25pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="line-height: 107%; font-size: small; mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">C'est le conteneur graphique des contrôles de l'application <o:p></o:p></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr style="mso-yfti-irow: 2; height: 29.25pt;"> | ||
| + | <td width="214" valign="top" style="width: 160.7pt; border: solid black 1.0pt; border-top: none; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 29.25pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="font-size: small;"><b style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Label</span></b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"> (étiquette) <o:p></o:p></span></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td width="406" valign="top" style="width: 304.75pt; border-top: none; border-left: none; border-bottom: solid black 1.0pt; border-right: solid black 1.0pt; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-left-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 29.25pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="line-height: 107%; font-size: small; mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Afficher un texte statique : un libellé. <o:p></o:p></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr style="mso-yfti-irow: 3; height: 57.8pt;"> | ||
| + | <td width="214" valign="top" style="width: 160.7pt; border: solid black 1.0pt; border-top: none; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 57.8pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="font-size: small;"><span class="SpellE"><b style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Text</span></b></span><b style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"> Box </span></b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"><o:p></o:p></span></span></p> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="line-height: 107%; font-size: small; mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">(zone de texte) <o:p></o:p></span></p> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 14.25pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="line-height: 107%; font-size: small; mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"><span style="mso-spacerun: yes;"> </span><o:p></o:p></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td width="406" valign="top" style="width: 304.75pt; border-top: none; border-left: none; border-bottom: solid black 1.0pt; border-right: solid black 1.0pt; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-left-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 57.8pt;"> | ||
| + | <p class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 3.0pt; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 0cm; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 150%;"><span style="line-height: 150%; font-size: small; mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Rentrer une valeur saisie, on peut aussi l'utiliser pour afficher du texte mais ce n'est pas recommandé. (utiliser plutôt le label pour l'affichage) <o:p></o:p></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr style="mso-yfti-irow: 4; height: 43.55pt;"> | ||
| + | <td width="214" valign="top" style="width: 160.7pt; border: solid black 1.0pt; border-top: none; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 43.55pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="font-size: small;"><span class="SpellE"><b style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Button</span></b></span><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"> (bouton de commande)<span style="mso-spacerun: yes;"> </span><o:p></o:p></span></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td width="406" valign="top" style="width: 304.75pt; border-top: none; border-left: none; border-bottom: solid black 1.0pt; border-right: solid black 1.0pt; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-left-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 43.55pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 3.5pt; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 0cm; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="line-height: 107%; font-size: small; mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Lancer l’exécution d'une procédure événementielle (généralement suite au <span class="SpellE">click</span> sur ce bouton) <o:p></o:p></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr style="mso-yfti-irow: 5; height: 15.0pt;"> | ||
| + | <td width="214" valign="top" style="width: 160.7pt; border: solid black 1.0pt; border-top: none; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 15.0pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="font-size: small;"><span class="SpellE"><b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">ListBox</span></b></span><b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"> <o:p></o:p></span></b></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td width="406" valign="top" style="width: 304.75pt; border-top: none; border-left: none; border-bottom: solid black 1.0pt; border-right: solid black 1.0pt; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-left-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 15.0pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="line-height: 107%; font-size: small; mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Afficher une liste de valeurs.<span style="mso-spacerun: yes;"> </span><o:p></o:p></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr style="mso-yfti-irow: 6; height: 29.3pt;"> | ||
| + | <td width="214" valign="top" style="width: 160.7pt; border: solid black 1.0pt; border-top: none; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 29.3pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: .9pt; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 0cm; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="font-size: small;"><span class="SpellE"><b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">ComboBox</span></b></span><b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"> <o:p></o:p></span></b></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td width="406" valign="top" style="width: 304.75pt; border-top: none; border-left: none; border-bottom: solid black 1.0pt; border-right: solid black 1.0pt; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-left-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 29.3pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="line-height: 107%; font-size: small; mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Combiner l’utilité des contrôles <span class="SpellE">ListBox</span> et <span class="SpellE">TextBox</span> <o:p></o:p></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr style="mso-yfti-irow: 7; height: 43.55pt;"> | ||
| + | <td width="214" valign="top" style="width: 160.7pt; border: solid black 1.0pt; border-top: none; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 43.55pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 5.25pt; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 0cm; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="font-size: small;"><span class="SpellE"><b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">PictureBox</span></b></span><b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"><span style="mso-spacerun: yes;"> </span><o:p></o:p></span></b></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td width="406" valign="top" style="width: 304.75pt; border-top: none; border-left: none; border-bottom: solid black 1.0pt; border-right: solid black 1.0pt; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-left-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 43.55pt;"> | ||
| + | <p class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 3.0pt; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 0cm; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 150%;"><span style="line-height: 150%; font-size: small; mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Afficher une image dans un cadre. (Il peut être redimensionné en fonction de l’image en utilisant <span class="SpellE">Autosize</span> = <span class="SpellE">True</span>) <o:p></o:p></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr style="mso-yfti-irow: 8; height: 43.55pt;"> | ||
| + | <td width="214" valign="top" style="width: 160.7pt; border: solid black 1.0pt; border-top: none; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 43.55pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 2.1pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="font-size: small;"><span class="SpellE"><b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">RadioButton</span></b></span><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"> (bouton radio) <o:p></o:p></span></span></p> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 14.25pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="line-height: 107%; font-size: small; mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"><span style="mso-spacerun: yes;"> </span><o:p></o:p></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td width="406" valign="top" style="width: 304.75pt; border-top: none; border-left: none; border-bottom: solid black 1.0pt; border-right: solid black 1.0pt; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-left-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 43.55pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 10.5pt; line-height: 107%;"><span style="font-size: small;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Sélectionner </span><span style="text-decoration: underline; text-underline: black;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-fareast-font-family: Calibri; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"></span></span><b style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">une seule</span></b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"> option parmi plusieurs. <o:p></o:p></span></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr style="mso-yfti-irow: 9; height: 29.25pt;"> | ||
| + | <td width="214" valign="top" style="width: 160.7pt; border: solid black 1.0pt; border-top: none; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 29.25pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%; tab-stops: center 29.6pt right 87.8pt;"><span style="font-size: small;"><b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Check Box</span></b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"> (case à cocher) <o:p></o:p></span></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td width="406" valign="top" style="width: 304.75pt; border-top: none; border-left: none; border-bottom: solid black 1.0pt; border-right: solid black 1.0pt; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-left-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 29.25pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 10.5pt; line-height: 107%;"><span style="font-size: small;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">choisir </span><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-fareast-font-family: Calibri; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"></span><b style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">une ou plusieurs<span style="text-decoration: underline; text-underline: black;"> </span></span></b><span style="text-decoration: underline; text-underline: black;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-fareast-font-family: Calibri; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"></span></span><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">options parmi d'autres. <o:p></o:p></span></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr style="mso-yfti-irow: 10; mso-yfti-lastrow: yes; height: 43.55pt;"> | ||
| + | <td width="214" valign="top" style="width: 160.7pt; border: solid black 1.0pt; border-top: none; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 43.55pt;"> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 7.25pt; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 0cm; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="font-size: small;"><span class="SpellE"><b style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">GroupBox</span></b></span><b style="mso-bidi-font-weight: normal;"><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"> </span></b><span style="mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; line-height: 107%; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"><span style="mso-spacerun: yes;"> </span><o:p></o:p></span></span></p> | ||
| + | <p align="left" class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 0cm; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 14.25pt; text-align: left; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 107%;"><span style="line-height: 107%; font-size: small; mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;"><span style="mso-spacerun: yes;"> </span><o:p></o:p></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td width="406" valign="top" style="width: 304.75pt; border-top: none; border-left: none; border-bottom: solid black 1.0pt; border-right: solid black 1.0pt; mso-border-top-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-left-alt: solid black .75pt; mso-border-alt: solid black .75pt; padding: .95pt 2.35pt 0cm 5.15pt; height: 43.55pt;"> | ||
| + | <p class="MsoNormal" style="margin-top: 0cm; margin-right: 1.2pt; margin-bottom: .0001pt; margin-left: 0cm; text-indent: 0cm; line-height: 150%;"><span style="line-height: 150%; font-size: small; mso-bidi-font-size: 12.0pt; mso-ascii-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-ascii-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-hansi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-hansi-theme-font: major-bidi; mso-bidi-font-family: 'Times New Roman'; mso-bidi-theme-font: major-bidi;">Regroupe un ensemble de contrôles graphique dans un seul cadre au sein du formulaire. <o:p></o:p></span></p> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </tbody> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
==== Propriétés ==== | ==== Propriétés ==== | ||
==== Instructions particulières ==== | ==== Instructions particulières ==== | ||
Version du 20 mai 2020 à 23:46
 Définition
Définition
Domaine, Discipline, Thématique
Définition écrite
Visual Basic .NET est un langage de programmation événementielle. Il est le successeur de Visual Basic 6.0. Il se compile et s’exécute sur l'architecture .NET(le framework .NET): les scripts VB 6.0 ne seront pas compilé en VB .NET. La première version fait ses débuts en 2002 (VB 7.0, Microsoft Visual Studio 2002, Framework .NET 1.0) et la dernière version en 2019 (VB 16.0, Microsoft Visual Studio 2019, Framework .NET 4.8). Visual Basic .NET permet le développement rapide d'applications Windows, de services web, de pages Web, l'accès aux bases de données…
|
Définition graphique
 Concepts ou notions associés
Concepts ou notions associés
 Exemples, applications, utilisations
Exemples, applications, utilisations
Les éléments de base de VB.Net
Comme toute langage de programmation, Visual Basic .NET permet de décrire des structures des données . Il offre un ensemble de notions telles que les variables, les constantes, les tableaux, les structures de contrôles et les procédures et les fonctions, qui peuvent être utilisées comme primitives pour développer des programmes.
Variable et constante
Notion de Variable
Les variables sont nécessaires pour stocker une valeur dynamique et réutilisable. C'est en fait une simple zone mémoire qui porte un nom choisi par le programmeur. Le nom de la variable est une adresse mémoire. Il faut déclarer chaque variable en précisant le type de celle-ci. La déclaration se fait avec le mot réservé Dim.
Syntaxe:
Dim <NomVariable> As <Type>
Pour la lisibilité du code on peut les commenter après une apostrophe ('). En ce qui concerne les noms des variables, on peut utiliser des majuscules, minuscules et chiffres. Les espaces et autres caractères spéciaux ne sont pas acceptés (accents, @, #). Le nom de la variable ne peut pas commencer par un chiffre.
Exemples:
Dim Ma_Variable As String Dim Nombre As Integer
Vous pouvez affecter des valeurs aux variables une fois qu’elles sont déclarées, comme montré dans l’exemple suivant :
Dim birthday As Date birthday = #3/9/1974# Dim birthday As Date = #3/9/1974# Dim goodNews As String = "Votre chèque est au courrier." Dim testCondition As Boolean = True
Vous pouvez déclarer des variables public, comme montré dans l’exemple suivant :
Public Ma_Variable As String
Lorsque vous créez une variable à l’aide de l’instruction Dim, Visual Basic initialise automatiquement les variables numériques sur 0, les chaînes de texte sur vide ("") et les variables de type date sur Janvier 1, 0001.
Les différents types de variables
Le langage VB utilise plusieurs types de données dont les plus utilisés sont le type String (chaîne de caractères), le type Integer (entier) et le type Single (décimal). Les types standards de données en VB sont résumés ci-dessous:
|
Type de variable |
Mémoire occupée |
Plage Utilisation principale |
|
Boolean |
2 octets |
Pour les conditions |
|
Byte
|
1 octet |
Pour les fichiers |
|
Char |
2 octets |
Pour les caractères |
|
Date |
8 octets |
Pour les dates |
|
Decimal
|
16 octets |
Pour les nombres décimaux |
|
Integer |
4 octets |
Pour les nombres entiers |
|
Long |
8 octets |
Pour les entiers longs |
|
Short |
2 octets |
Pour les entiers courts |
|
Single |
4 octets |
Pour les grands nombres à virgules (avec simple précision) |
|
String |
Variable |
Pour les chaînes de caractères |
Déclaration des constantes
Pour déclarer une constante, utilisez l’instruction Const avec la syntaxe suivante :
Syntaxe:
Const NomConstant As Type
Exemple:
Dim surface, rayon, périmètre As Double Const Pi As Double = 3.1415 surface = Pi * rayon ^ 2 périmètre = 2 * Pi * rayon
Les tableaux
Un tableau est une séquence d’éléments de données appartenant à un même type. Vous pouvez accéder aux éléments individuels d’un tableau en utilisant le nom du tableau et un ou plusieurs index (commençant à 0) pour spécifier la position de l’élément dans le tableau. Un tableau peut présenter une ou plusieurs dimensions avec un ou plusieurs éléments dans chaque dimension.
Déclaration d’un tableau unidimensionnel
Vous déclarez un tableau en spécifiant les éléments suivants :
- Nom du tableau
- Taille (nombre d’éléments)
- Type de données des éléments du tableau
- Modificateur d’accès (si nécessaire)
Syntaxe:
ModificateurAccès NomTableau(N) As <Type>
Cette instruction déclare un tableau NomTableau de taille N+1. Pour accéder au i ème élément du tableau, il faut préciser l’indice entre parenthèses comme suit : NomTableau(i-1), i doit être compris dans l’intervalle [0, N].
Vous pouvez déclarer des tableaux locaux au moyen de l’instruction Dim et en intégrant la déclaration à l’intérieur d’une procédure. Pour créer un tableau public, utilisez le mot clé Public à la place de Dim.
Exemples de déclarations d’un tableau local:
Sub initialisation( )
'Allouer 31 éléments (0) à (30)
Dim Tab(30) As Decimal
Dim number As Integer
For number = 0 to 30
Tab(number) = 100
Next number
End Sub
Exemples de déclarations d’un tableau public:
Public entiers(14) As Integer
Public réels(20) As Double
Public entiers( ) As Integer = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
Public Grille ( , ) As Integer ={{1,2},{3,4}}
Déclaration de tableaux multidimensionnels
Pour déclarer une variable de tableau multidimensionnel, ajoutez une paire de parenthèses après le nom de la variable et utilisez des virgules à l’intérieur pour séparer les dimensions.
Exemple:
Dim 2DArray(3,2) As Double 2DArray(2,1) = 23 2DArray(2,2) = 17
Dans Visual Basic .NET, vous pouvez redimensionner un tableau à tout moment en lui spécifiant une nouvelle grandeur. Vous pouvez même changer le nombre de dimensions du tableau.
Syntaxe:
ReDim tableauExistant ( NouvelleGrandeur )
Structures de contrôle
Structures conditionnelles
Forme simple
Syntaxe:
If condition(s) Then
Instruction(s)
Else
Instruction(s)
End IF
Exemple:
If Moyenne >= 12 Then
Admis = Admis + 1
Console.WriteLine (" Candidat admis ")
Else
Ajournes = Ajournes + 1
Console.WriteLine (" Candidat ajourné ")
End If
on peut utiliser IIF
Syntaxe:
IIf (Condition, ValeurSiVrai, ValeurSiFaux)
Exemple:
Dim Note As Single
Dim Reponse As String
Console.Write(" Tapez votre note: ")
Note = Console.Read()
Reponse = IIf(Note >= 10, " Admis ", " Ajourné ")
Console.WriteLine(Reponse)
Forme imbriqué
Syntaxe:
If condition(s) Then
Instruction(s)
If condition Then
Instruction(s)
Else If condition Then
Instruction(s)
Else condition Then
Instruction(s)
End IF
Else
Instruction(s)
End IF
Exemple:
If NombrePropose > NombreATrouver Then
Console.WriteLine("Votre nombre est trop grand !")
ElseIf NombrePropose < NombreATrouver Then
Console.WriteLine("Votre nombre est trop petit !")
Else
Console.WriteLine("Gagné !")
End If
Structure à choix
Syntaxe:
Select Case expression Case Liste_Valeurs_1
Instruction(s)
Case Liste_Valeurs_2
Instruction(s)
Case Else
Instruction(s)
End Select
Exemple:
Select Case CodeASCIICaractère
Case 65, 69, 73, 79, 85
Console.WriteLine(" C’est une voyelle ")
Case 66 To 90
Console.WriteLine(" C’est une consonne ")
Case Else
Console.WriteLine(" Ce n’est pas une lettre ")
End Select
Structures itératives
Les instructions répétitives sont utilisées pour boucler sur une suite d’instructions.
Structure complète
Si le nombre de boucles est connu à l’avance, on utilise l'instruction For … To … Next.
Syntaxe:
For Compteur = Début To Fin [Step Incrément]
Instruction(s)
[ ... Exit For] 'pour une interruption préalable de la boucle
[Instruction(s)]
Next [Compteur] 'le mot Compteur est facultatif
Exemple:
Dim i As Integer
For i = 1 To 12
Console.WriteLine(i * 2)
Next i 'le i n’est pas obligatoire
On peut utiliser For … Each … Next. C'est une extension de la boucle For … To … Next.
Syntaxe:
For Each Elément In Ensemble
Instruction(s)
[ ... Exit For]
[Instruction(s)]
Next [Elément]
Exemple:
Dim numbers() As Integer = {1, 4, 7}
Dim letters() As String = {"a", "b", "c"}
For Each number As Integer In numbers
For Each letter As String In letters
Console.Write(number.ToString & letter & " ")
Next
Next
Structure à condition d'arrêt
Test antérieur
La condition est ici testée au début, c'est-à-dire à l’entrée de la boucle. Avec Do while … Loop, la boucle est répétée tant que la condition est vraie. Si la condition n’est pas vraie au départ, les instructions de la boucle ne sont pas exécutées.
Syntaxe:
Do While Condition
Instruction(s)
[... Exit Do]
[Instruction(s)]
Loop
Exemple:
Do While MotPropose <> MotDePasse
MotPropose = InputBox("Donnez votre mot de passe")
Loop
De même avec Do Until … Loop
Syntaxe:
Do Until Condition
Instruction(s)
[... Exit Do]
[Instruction(s)]
Loop
Exemple:
Do Until MotPropose = MotDePasse
MotPropose = InputBox("Donnez votre mot de passe")
Loop
Test postérieur
La condition est ici testée à la fin de la boucle. Avec Do … Loop While, la boucle est répétée tant que la condition est vraie. Les instructions de la boucle sont donc exécutées au moins une fois.
Syntaxe:
Do
Instruction(s)
[... Exit Do]
[Instruction(s)]
Loop While Condition
Exemple:
Do
MotPropose = InputBox("Donnez votre mot de passe")
Loop While MotPropose <> MotDePasse
De même avec Do … Loop Until
Syntaxe:
Do
Instruction(s)
[... Exit Do]
[Instruction(s)]
Loop Until Condition
Exemple:
Do
MotPropose = InputBox("Donnez votre mot de passe")
Loop Until MotPropose = MotDePasse
Procédure et fonction
Les procédures
VB.NET permet l’utilisation des procédures et des fonctions avec ou sans paramètres. Rappelez-vous que la grande différence entre la procédure et la fonction est que cette dernière retourne une valeur lorsqu’elle est appelée.
Passage par valeur
Pour transmettre un paramètre par valeur, celui-ci doit être obligatoirement précédé par le mot réservé ByVal. Dans ce cas si la procédure appelée modifie la valeur de la variable d'origine, la valeur initiale de la variable ne change pas. Lorsque l'exécution revient à la procédure appelante, la variable contient la valeur qu'elle avait avant la transmission de la valeur.
Syntaxe:
Private Sub NomProcédure( ByVal argument As Type, … )
Instruction(s)
End Sub
Exemple:
Private Sub Permutation(ByVal valeur1 As Integer, ByVal valeur2 As Integer)
Dim variable As Integer
variable = valeur1
valeur1 = valeur2
valeur2 = variable
End Sub
L’appel de la procédure se fait soit en inscrivant Call suivi du nom de la procédure, et des paramètres à lui transmettre, soit en écrivant uniquement le nom de la procédure, suivi des paramètres à lui transmettre.
Exemple:
Dim X, Y As Integer
X = InputBox("Donnez 1er entier: ")
Y = InputBox("Donnez 2ème entier: ")
Console.WriteLine("Avant permutation X = " & X & " et Y = " & Y )
Call Permutation(X, Y)
Console.WriteLine("Après permutation X = " & X & " et Y = " & Y )
Passage par référence
Si le paramètre est précédé par le mot réservé ByRef, la variable est transmise par référence (c à d a travers l’adresse des données en mémoire). Ainsi, toute modification de la variable locale correspondante dans la procédure se reflète sur la variable utilisée lors de l’appel.
Dans l'exemple précédant on remplace ByVal par ByRef
Les fonctions
Lors de la déclaration d'une fonction, la valeur qui doit être retournée par celle-ci doit être affectée au nom de la fonction. La déclaration de la fonction se termine par les mots réservés End function.
Syntaxe:
Private function NomFonction( Argument As Type, … ) As Type
Instruction(s)
NomFonction = RésultatDeLaFonction ‘ou bien return RésultatDeLaFonction
End function
Exemple:
Private function Somme( valeur1 As Integer, valeur2 As Integer ) As integer Somme = Valeur1 + valeur2 End function
L’appel suivant retourne la somme de X et Y et affecte le résultat à la variable Z.
Exemple:
Dim X, Y, Z As Integer X = 10 Y = 20 Z = Somme(X, Y)
Orienté objet Visual Basic .Net
Classe et objet
Un objet est une entité qui contient des données qui définissent son état (on les appelle des propriétés) et des fonctions (on les appelle des méthodes). Un objet est créé selon un modèle qu'on appelle une classe. donc on les appellera des objets ou des instances de classes.
Exemple de classe:
Public Class personne
' attributs
Private prenom As String
Private nom As String
Private age As Integer
' méthode
Public Sub initialise(ByVal P As String, ByVal N As String, ByVal age As Integer)
Me.prenom = P
Me.nom = N
Me.age = age
End Sub
' méthode
Public Sub identifie()
Console.WriteLine ((prenom & "," & nom & "," & age))
End Sub
End Class
Pour que p1 référence un objet de la classe personne, il faut écrire :
Dim p1 as personne=new personne()
Cela a pour effet de créer un objet de type personne non encore initialisé : les attributs nom et prenom qui sont des références d'objets de type String auront la valeur nothing, et age la valeur 0. Il y a donc une initialisation par défaut. Maintenant que p1 référence un objet, l'instruction d'initialisation de cet objet suivante est valide :
p1.initialise("Tounsi","Ali",22)
Constructeur et destructeur
Un constructeur est une procédure qui porte le nom New et qui est appelée lors de la création de l'objet. On s'en sert généralement pour l'initialiser.
Exemple :
Public Class personne
' attributs
Private prenom As String
Private nom As String
Private age As Integer
' constructeurs
Public Sub New(ByVal P As String, ByVal N As String, ByVal age As Integer)
initialise(P, N, age)
End Sub
Public Sub New(ByVal P As personne)
initialise(P)
End Sub
' méthodes d'initialisation de l'objet
Public Sub initialise(ByVal P As String, ByVal N As String, ByVal age As Integer)
Me.prenom = P
Me.nom = N
Me.age = age
End Sub
Public Sub initialise(ByVal P As personne)
prenom = P.prenom
nom = P.nom
Me.age = P.age
End Sub
' méthode
Public Sub identifie()
Console.WriteLine((prenom & "," & nom & "," & age))
End Sub
End Class
Voici un court programme de test :
Sub Main()
Dim p1 As New personne("Tounsi", "Rania", 30)
Console.Write("p1=")
p1.identifie()
Dim p2 As New personne(p1)
Console.Write("p2=")
p2.identifie()
End Sub
les résultats obtenus :
p1=tounsi,Rania,30 p2=tounsi,Rania,30
Un destructeur est une procédure qui est automatiquement exécutée à la mort de l'objet. Une telle procédure se nomme Finalize().
Protected Overrides Sub Finalize( ) 'Peut fermer des connexions ou d’autres ressources conn.Close End Sub
Encapsulation
L'encapsulation est un concept important de la Programmation Orientée Objet. Il permet de rassembler des données(attributs) et des traitements(méthodes) dans une seule entité (classe) et interdit d'agir directement sur les données d'un objet sauf à l'aide des méthodes. En général, les attributs d'une classe sont déclarées privées alors que ses méthodes sont déclarées publiques.
- Private: Un champ privé n'est accessible que par les seules méthodes internes de la classe.
- Public : Un champ public est accessible par toute fonction définie ou non au sein de la classe.
- Protected : Un champ protégé n'est accessible que par les seules méthodes internes de la classe
Nous rajoutons à la classe personne les méthodes nécessaires pour lire ou modifier l'état des attributs des objets.
' accesseurs
Public Function getPrenom() As String
Return prenom
End Function
Public Function getNom() As String
Return nom
End Function
Public Function getAge() As Integer
Return age
End Function
'modifieurs
Public Sub setPrenom(ByVal P As String)
Me.prenom = P
End Sub
Public Sub setNom(ByVal N As String)
Me.nom = N
End Sub
Public Sub setAge(ByVal age As Integer)
Me.age = age
End Sub
Nous testons la nouvelle classe avec le programme suivant :
Sub Main()
Dim P As New personne("Tounsi", "Sami", 25)
Console.WriteLine(("P=(" & P.getPrenom() & "," & P.getNom() & "," & P.getAge() & ")"))
P.setAge(30)
Console.WriteLine(("P=(" & P.getPrenom() & "," & P.getNom() & "," & P.getAge() & ")"))
End Sub
Il existe une autre façon d'avoir accès aux attributs d'une classe c'est de créer des propriétés. Une propriété Property est une méthode particulière permet de lire (get) ou de fixer (set) la valeur d'un attribut. Il est conseillé de mettre un '_' au début du nom d'un attribut privée puis une majuscule au début de chaque mot sauf le premier afin que les propriétés portent le nom des attributs primitifs. En effet, une propriété ne peut porter le même nom que l'attribut qu'elle gère pour éviter un conflit de noms dans la classe.
' attributs
Private _prenom As String
Private _nom As String
Private _age As Integer
...
' propriétés
Public Property prenom() As String
Get
Return _prenom
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As String)
_prenom = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Property nom() As String
Get
Return _nom
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As String)
_nom = Value
End Set
End Property
Public Property age() As Integer
Get
Return _age
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As Integer)
If Value >= 0 Then
_age = Value
Else
Throw New Exception("âge (" & Value & ") invalide")
End If
End Set
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property identifie() As String
Get
Return "personne(" & _prenom & "," & _nom & "," & age & ")"
End Get
End Property
Remarque: Dans une classe, les membres partagés (propriétés et méthodes) peuvent être appelés directement, sans passer par l'instanciation d'un objet. Le mot-clé Shared indique en effet que la propriété ou méthode ne s'appuie pas sur un objet spécifique mais bien sur la classe elle-même ce qu'on appelles méthodes et attributs de classe ou méthodes et attributs partagées
' attributs de classe
Private Shared _nbPersonnes As Long = 0
...
' constructeurs
Public Sub New(ByVal P As String, ByVal N As String, ByVal age As Integer)
' une personne de plus
_nbPersonnes += 1
Me._prenom = P
Me._nom = N
Me._age = age
End Sub
Public Sub New(ByVal P As personne)
' une personne de plus
_nbPersonnes += 1
Me._prenom = P._prenom
Me._nom = P._nom
Me._age = P._age
End Sub
' propriété de classe
Public Shared ReadOnly Property nbPersonnes() As Long
Get
Return _nbPersonnes
End Get
End Property
...
Nous testons le programme suivant :
Sub Main()
Dim p1 As New personne("Tounsi", "Samir", 26)
Dim p2 As New personne(p1)
Console.WriteLine(("Nombre de personnes créées : " & personne.nbPersonnes))
End Sub
Surcharge
La surcharge est une technique simple à utiliser, qui permet d'utiliser le même nom de fonction avec des paramètres de différents types.
Exemple:
Class Addition
Overloads Public Sub Add(a as Integer, b as Integer)
Console.Writeline ("Somme de deux entiers: " + Convert.ToString(a + b))
End Sub
Overloads Public Sub Add(a as String, b as String)
Console.Writeline ("concatination de deux chaines: " + a + b)
End Sub
End Class
Shared Sub Main()
'Créée l'objet
Dim monCalcul as Addition
monCalcul = New Addition
'Appel de la première fonction
monCalcul.Add(10, 20)
'Appel de la seconde fonction :
monCalcul.Add("Bonjour", " comment allez-vous ?")
End Sub
Héritage
L'héritage est un mécanisme par lequel une classe dérivée (ou classe fille) hérite toutes les caractéristiques de sa classe de base (ou classe mère) et ajoute celles qui lui sont propres . Il suffit pour cela d'utiliser le mot-clé Inherits.
Exemple:
Public Class enseignant Inherits personne
' attributs
Private _section As Integer
' constructeur
Public Sub New(ByVal P As String, ByVal N As String, ByVal age As Integer, ByVal section
As Integer)
MyBase.New(P, N, age)
Me._section = section
End Sub
' propriété section
Public Property section() As Integer
Get
Return _section
End Get
Set(ByVal Value As Integer)
_section = Value
End Set
' surcharge propriété identifie
Public Shadows ReadOnly Property identifie() As String
Get
Return "enseignant(" & MyBase.identifie & "," & _section & ")"
End Get
End Property
End Class
Nous testons le programme suivant :
Sub Main()
Console.WriteLine(New enseignant("Tounsi", "Samia", 40, 27).identifie)
End Sub
Polymorphisme
La notion de polymorphisme est très liée à celle d’héritage. Grâce à la redéfinition, il est possible de redéfinir une méthode dans des classes héritant d’une classe de base. Par ce mécanisme, une classe qui hérite des méthodes d’une classe de base peut modifier le comportement de certaines d'entre elles pour les adapter à ses propres besoins.
Exemple, Supposons qu’on a une classe appelée Taxe_Base, qui fournit les fonctionnalités de base pour calculer les taxes. Les classes dérivées de Taxe_Base (Taxe_Entreprise ou Taxe_Douane, par exemple) pourraient implémenter des méthodes telles que CalculerTaxe.
Programmation évènementielle Visual Basic .Net
Principe de la programmation événementielle
A part la programmation séquentielle, où les instructions s’exécutent de manière séquentielle, on peut utiliser VB.NET pour réaliser de la programmation par événements, c’est à dire programmer des procédures qui s’exécutent quand un événement est déclenché. La plupart du temps, l’événement est déclenché par l’utilisateur du programme.
- Partie visuelle: des fenêtres, des boutons, des labels. C'est ce qui est vu par l'utilisateur final de l'application.
- Code VB.NET "derrière" la partie visuelle. C'est au développeur de réaliser cette partie.
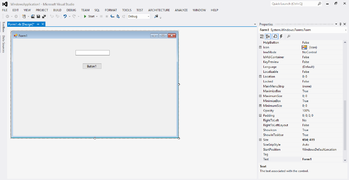
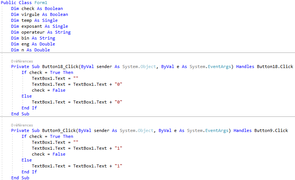
Exemple : Mini Calculatrice
L'utilisateur de l'application va interagir avec la fenêtre de la mini-calculatrice.
- L'utilisateur saisi deux entiers
- Il clique sur un bouton d'addition ou de soustraction
- Le système affiche le résultat
la procédure événementielle générée pour un objet suit la syntaxe suivante:
Private Sub NomObjet_NomEvénement (paramètres)
Instructions
End Sub
Généralités sur les contrôles
Contrôles standards
La partie visuelle du projet est composée principalement d'un ou de plusieurs formulaires (Forms). Un formulaire représente une fenêtre (Window). Dans ce formulaire, on va ajouter les éléments graphiques dont on a besoin.
<tbody> </tbody>|
Nom de l'élément<o:p></o:p> |
Utilité<o:p></o:p> |
|
Form (feuille) <o:p></o:p> <o:p></o:p> |
C'est le conteneur graphique des contrôles de l'application <o:p></o:p> |
|
Label (étiquette) <o:p></o:p> |
Afficher un texte statique : un libellé. <o:p></o:p> |
|
Text Box <o:p></o:p> (zone de texte) <o:p></o:p> <o:p></o:p> |
Rentrer une valeur saisie, on peut aussi l'utiliser pour afficher du texte mais ce n'est pas recommandé. (utiliser plutôt le label pour l'affichage) <o:p></o:p> |
|
Button (bouton de commande) <o:p></o:p> |
Lancer l’exécution d'une procédure événementielle (généralement suite au click sur ce bouton) <o:p></o:p> |
|
ListBox <o:p></o:p> |
Afficher une liste de valeurs. <o:p></o:p> |
|
ComboBox <o:p></o:p> |
Combiner l’utilité des contrôles ListBox et TextBox <o:p></o:p> |
|
PictureBox <o:p></o:p> |
Afficher une image dans un cadre. (Il peut être redimensionné en fonction de l’image en utilisant Autosize = True) <o:p></o:p> |
|
RadioButton (bouton radio) <o:p></o:p> <o:p></o:p> |
Sélectionner une seule option parmi plusieurs. <o:p></o:p> |
|
Check Box (case à cocher) <o:p></o:p> |
choisir une ou plusieurs options parmi d'autres. <o:p></o:p> |
|
GroupBox <o:p></o:p> <o:p></o:p> |
Regroupe un ensemble de contrôles graphique dans un seul cadre au sein du formulaire. <o:p></o:p> |
Propriétés
Instructions particulières
Exemple Pratique
 Erreurs ou confusions éventuelles
Erreurs ou confusions éventuelles
- Confusion entre VB et VB .NET
- Confusion entre IDE et Framework
- Confusion entre procédure et fonction
- Confusion entre passage des paramètres par valeur et par référence
- Confusion entre surcharge et redéfinition
- Erreur fréquente: mal utilisation de la portée des objets
- Erreur fréquente: chois de la structure conditionnelle adéquate
- Erreur fréquente: chois de la structure itérative adéquate
- Difficulté: mal appropriation de la notion d'encapsulation
- Difficulté: mal appropriation de la notion d'héritage
- Difficulté: mal appropriation de la notion de polymorphisme
 Questions possibles
Questions possibles
- Quelles sont les principales différences entre VB et VB.NET?
- Qu’est-ce qu’un IDE?
- A quoi sert un IDE?
- Qu’est-ce que Visual Studio?
- Qu’est-ce qu’un Framework?
- A quoi sert un Framework?
- Qu’est-ce qu’un Framework .NET?
- Quelle est l’architecture de Framework .NET?
- Comment déclarer une variable? Donner 3 exemples avec 3 types différents.
- Qu’est-ce qu’une variable public? Donner un exemple.
- Comment déclarer une constante? Donner un exemple.
- Comment déclarer un tableau unidimensionnel local? Donner un exemple.
- Comment déclarer un tableau unidimensionnel public? Donner un exemple.
- Comment manipuler un tableau unidimensionnel? Donner un exemple.
- Comment déclarer un tableau multidimensionnel? Donner un exemple.
- Dans Visual Basic .NET, vous pouvez redimensionner un tableau? Si oui, comment?
- Quelles sont les formes possibles de structures conditionnelles? Donner des exemples
- Quelle est la différence entre une structure itérative complète et celle à condition d'arrêt? Donner des exemples
- Quelle est la différence entre une structure itérative à condition d'arrêt avec test antérieur et celle avec test postérieur
- Quelle est la différence entre procédure et fonction? Donner des exemples
- Quelle est la différence entre le passage des paramètre par valeur et celui par référence? Donner des exemples
 Liaisons enseignements et programmes
Liaisons enseignements et programmes
Idées ou Réflexions liées à son enseignement
- Il faut toujours cerner des savoirs relatifs aux spécificités du langage VB .NET. Par exemple:
- VB ne possède qu’un seul opérateur = contrairement à d'autres langages tel que C# qui possède un opérateur d’affectation et un opérateur d’égalité.
- Dans Visual Basic .NET, vous pouvez redimensionner un tableau à tout moment en lui spécifiant une nouvelle grandeur. Vous pouvez même changer le nombre de dimensions du tableau.
- Une discussion collective entres les apprenants, faire apprendre le choix de la bonne structure de contrôle.
- chois de la structure conditionnelle adéquate.
- chois de la structure itérative adéquate.
- On utilise les « schémas » qui sont les structures utilisées dans le traitement des informations pour expliquer quelques concepts:
- Pour expliquer les structures de contrôle.
- Pour expliquere la notion d'héritage.
Aides et astuces
Education: Autres liens, sites ou portails
 Bibliographie
Bibliographie
Pour citer cette page: (Basic .NET)
ABROUGUI, M & al, 2020. Visual Basic .NET. In Didaquest [en ligne]. <http:www.didaquest.org/wiki/Visual_Basic_.NET>, consulté le 3, décembre, 2024
- « Visual Basic ». In Wikipédia, 20 avril 2020. https://fr.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Visual_Basic&oldid=169803403.
- Kalumba, Etienne. « Formation Visual Basic Net ».Visual Basic.NET En 21 Jours, Ducan Mackenzie, Kent Sharkey, Campus Press, 2002, ISBN: 2-7440-1369-2. Consulté le 3 mai 2020. https://www.academia.edu/38476347/Formation_visual_basic_net.
- cours-gratuit.com. « [PDF] Tutoriel avancé du langage Visual Basic .NET
- Informatique (Concepts)
- Génie logiciel (Concepts)
- Programmation (Concepts)
- Orientée Objet (Concepts)
- Programmation événementielle (Concepts)
- IDE
- Microsoft Visual Studio
- Framework
- Framework .NET
- Langage de programmation
- Paradigme de programmation
- Orientée Objet
- Programmation événementielle
- Concepts
- Programmation informatique