Différences entre versions de « Nouns »
| (Une version intermédiaire par le même utilisateur non affichée) | |||
| Ligne 95 : | Ligne 95 : | ||
{{Commons}} [https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?search={{PAGENAMEE}} {{PAGENAME}}] | {{Commons}} [https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?search={{PAGENAMEE}} {{PAGENAME}}] | ||
{{Goc}} [https://www.goconqr.com/en/search?q={{PAGENAMEE}} {{PAGENAME}}] | {{Goc}} [https://www.goconqr.com/en/search?q={{PAGENAMEE}} {{PAGENAME}}] | ||
| − | {{cc}} | + | {{cc}} [https://cmapscloud.ihmc.us:443/rid=20WJG4MM3-21YSX0V-LM7M14 : carte conceptuelle (cmap)] |
{{pdf}} Document PDF [https://www...... {{PAGENAME}}: Document PDF] | {{pdf}} Document PDF [https://www...... {{PAGENAME}}: Document PDF] | ||
{{fig}} Image/Figure [https://www...... {{PAGENAME}}: Titre de l'image ou de la figure] | {{fig}} Image/Figure [https://www...... {{PAGENAME}}: Titre de l'image ou de la figure] | ||
Version actuelle datée du 13 novembre 2024 à 19:52
 Traduction
Traduction
Noms (Français) / Nouns (Anglais) / أسماء (Arabe) / Sustantivos (Espagnol) / Substantivos (Portugais) / Существительные (Russe) / Sostantivi (Italien) / Nomen (Allemand) / 名词 (Chinois (Mandarin)) / संज्ञा (Hindi) / 名詞 (Japonais) / বিশেষ্য (Bengali)
 Définition
Définition
Domaine, Discipline, Thématique
Définition écrite
![]() Basic Definition
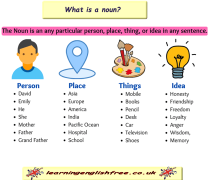
A noun is a word that designates a person, place, object, or idea.
Basic Definition
A noun is a word that designates a person, place, object, or idea.
![]() Intermediate Definition
A noun is a grammatical category that serves to identify and designate concrete or abstract entities. It can be classified into different subcategories, such as proper nouns, which refer to unique individuals, and common nouns, which refer to classes of objects or ideas.
Intermediate Definition
A noun is a grammatical category that serves to identify and designate concrete or abstract entities. It can be classified into different subcategories, such as proper nouns, which refer to unique individuals, and common nouns, which refer to classes of objects or ideas.
![]() Advanced Definition
The noun, as a fundamental element of language, plays a crucial role in structuring discourse. It can be analyzed across several dimensions: syntactically, where it often functions as the subject or object in a sentence; semantically, where it conveys specific meanings; and pragmatically, where its usage varies according to social and cultural context. Nouns may also be affected by morphological properties such as gender and number.
Advanced Definition
The noun, as a fundamental element of language, plays a crucial role in structuring discourse. It can be analyzed across several dimensions: syntactically, where it often functions as the subject or object in a sentence; semantically, where it conveys specific meanings; and pragmatically, where its usage varies according to social and cultural context. Nouns may also be affected by morphological properties such as gender and number.
![]() In-Depth Definition
A noun is an essential lexical unit within linguistic systems that serves to reference both concrete and abstract entities. Syntactically, it can function as a subject, direct or indirect object, and complement. Semantically, nouns are divided into categories such as proper nouns (which denote specific individuals or locations) and common nouns (which encompass classes of objects or ideas). Morphologically, they are subject to variations in gender (masculine or feminine) and number (singular or plural), influencing their agreement with other elements in the sentence. Furthermore, from a pragmatic perspective, the use of nouns is contextually determined and can vary according to social and cultural conventions. This complexity underscores the importance of nouns in constructing meaning and facilitating human communication.
}}
In-Depth Definition
A noun is an essential lexical unit within linguistic systems that serves to reference both concrete and abstract entities. Syntactically, it can function as a subject, direct or indirect object, and complement. Semantically, nouns are divided into categories such as proper nouns (which denote specific individuals or locations) and common nouns (which encompass classes of objects or ideas). Morphologically, they are subject to variations in gender (masculine or feminine) and number (singular or plural), influencing their agreement with other elements in the sentence. Furthermore, from a pragmatic perspective, the use of nouns is contextually determined and can vary according to social and cultural conventions. This complexity underscores the importance of nouns in constructing meaning and facilitating human communication.
}}
Définition graphique
- AUTRES MEDIAS
![]() Nouns (Discipline)
Nouns (Discipline)
![]() Nouns: (Discipline)
Nouns: (Discipline)
![]() Nouns: (Discipline)
Nouns: (Discipline)
![]() Nouns: (Discipline)
Nouns: (Discipline)
![]() Nouns: (Discipline)
Nouns: (Discipline)
![]() Nouns
Nouns
![]() Nouns
Nouns
![]() : carte conceptuelle (cmap)
: carte conceptuelle (cmap)
![]() Document PDF Nouns: Document PDF
Document PDF Nouns: Document PDF
![]() Image/Figure Nouns: Titre de l'image ou de la figure
Image/Figure Nouns: Titre de l'image ou de la figure
 Concepts ou notions associés
Concepts ou notions associés
Noun Phrase / Proper Nouns / Common Nouns / Collective Nouns / Abstract Nouns / Concrete Nouns / Countable Nouns / Uncountable Nouns / Gender in Nouns / Number Agreement / Case in Nouns / Noun Functions / Syntax of Nouns / Morphology of Nouns / Semantic Roles of Nouns / Noun Modifiers / Determiners with Nouns / Possessive Nouns / Noun Clauses / Compounding in Nouns / Derivation of Nouns / Inflection of Nouns / Nominalization / Language Acquisition of Nouns / Pragmatics of Noun Usage /
 Exemples, applications, utilisations
Exemples, applications, utilisations
................................................................................ ................................................................................ ................................................................................
................................................................................ ................................................................................ ................................................................................ |
 Erreurs ou confusions éventuelles
Erreurs ou confusions éventuelles
![]() Exemples de difficultés de compréhension ou d'interprétation courantes:
Exemples de difficultés de compréhension ou d'interprétation courantes:
- .........................................
- .........................................
![]() Confusions ou glissement de sens potentiels
Confusions ou glissement de sens potentiels
- Confusion entre ....... - ........
- Confusion entre ....... - ........
- .........................................
- .........................................
 Questions possibles
Questions possibles
 Liaisons enseignements et programmes
Liaisons enseignements et programmes
Idées ou Réflexions liées à son enseignement
Education: Autres liens, sites ou portails
 Bibliographie
Bibliographie
Pour citer cette page: ([1])
ABROUGUI, M & al, 2024. Nouns. In Didaquest [en ligne]. <http:www.didaquest.org/wiki/Nouns>, consulté le 21, novembre, 2024
- ..................
- ..................
- ..................
- ..................
- Pages utilisant des arguments dupliqués dans les appels de modèle
- Sponsors Education
- Linguistics (Concepts)
- Psycholinguistics (Concepts)
- Morphology (Concepts)
- Syntax (Concepts)
- Semantics (Concepts)
- Pragmatics (Concepts)
- Lexicology (Concepts)
- Sociolinguistics (Concepts)
- Computational Linguistics (Concepts)
- Semiotics (Concepts)
- Noun Phrase
- Proper Nouns
- Common Nouns
- Collective Nouns
- Abstract Nouns
- Concrete Nouns
- Countable Nouns
- Uncountable Nouns
- Gender in Nouns
- Number Agreement
- Case in Nouns
- Noun Functions
- Syntax of Nouns
- Morphology of Nouns
- Semantic Roles of Nouns
- Noun Modifiers
- Determiners with Nouns
- Possessive Nouns
- Noun Clauses
- Compounding in Nouns
- Derivation of Nouns
- Inflection of Nouns
- Nominalization
- Language Acquisition of Nouns
- Pragmatics of Noun Usage
- Concepts
- Nouns
- Nouns (Concepts)
- Fiche conceptuelle didactique