Différences entre versions de « Ecodriving »
| (14 versions intermédiaires par le même utilisateur non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 33 : | Ligne 33 : | ||
|Définition= <!-- Ne pas Modifier --> | |Définition= <!-- Ne pas Modifier --> | ||
<!-- *************** Commercez les modifications *******************--> | <!-- *************** Commercez les modifications *******************--> | ||
| + | ''' | ||
| + | Ecodriving: A Responsible and Sustainable Driving Approach''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Detailed Definition: | ||
| + | Ecodriving, or "eco-driving," refers to a set of driving practices and behaviors aimed at reducing fuel consumption, minimizing greenhouse gas emissions, and extending vehicle lifespan. This approach combines technical and behavioral principles to enable driving that is more environmentally friendly while optimizing costs for the driver. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Main Objectives of Ecodriving: | ||
| + | Reducing Pollutant Emissions: Lowering fuel consumption decreases CO₂ emissions, fine particles, and other pollutants harmful to health and the environment. | ||
| + | Resource Optimization: Smooth, anticipatory driving reduces wear on tires, brakes, and other vehicle components. | ||
| + | Financial Savings: Lower fuel consumption results in direct savings, while reduced wear decreases maintenance costs. | ||
| + | Improved Road Safety: Adopting preventive and calmer driving habits reduces the risk of accidents. | ||
| + | Core Principles of Ecodriving: | ||
| + | Anticipation and Observation: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Observe traffic conditions carefully to foresee slowdowns or stops. | ||
| + | Maintain a safe following distance to avoid sudden braking and ensure smooth driving. | ||
| + | Speed Management: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Drive at a moderate and consistent speed, suited to traffic conditions. | ||
| + | Avoid sudden accelerations and unnecessary braking. | ||
| + | Optimal Gear Usage: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Shift to higher gears as soon as possible (typically between 2,000–2,500 RPM for gasoline engines and 1,500–2,000 RPM for diesel engines). | ||
| + | Drive in low RPMs when possible without overloading the engine. | ||
| + | Reducing Unnecessary Loads: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Remove excess weight from the vehicle (unneeded luggage, unused roof racks, etc.). | ||
| + | Ensure tires are properly inflated to the recommended pressure. | ||
| + | Strategic Use of Equipment: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Limit excessive use of air conditioning or heating, which increases fuel consumption. | ||
| + | Turn off the engine during extended stops (e.g., at traffic lights or in traffic jams). | ||
| + | Trip Planning: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Choose the shortest, most fluid routes to minimize stops and starts. | ||
| + | Avoid peak traffic hours when possible. | ||
| + | Benefits of Ecodriving: | ||
| + | Environmental: Significant reduction in pollutant emissions. | ||
| + | Economic: Fuel savings of up to 20% depending on driving habits. | ||
| + | Comfort: Smoother, more fluid driving reduces stress behind the wheel. | ||
| + | Durability: Conservation of resources and reduced long-term ecological impact. | ||
| + | Relevance and Modern Context: | ||
| + | Given the urgency of the climate crisis and rising energy costs, Ecodriving has become increasingly important. It aligns with broader sustainable mobility efforts, complementing initiatives such as electric vehicle adoption and the promotion of public transport. Many governments and organizations actively promote Ecodriving through awareness campaigns, specialized training, and financial incentives. | ||
| + | Ecodriving: A Comprehensive Definition of Responsible and Sustainable Driving | ||
| + | |||
| + | Definition: | ||
| + | Ecodriving, or "eco-driving," encompasses a set of techniques and habits aimed at reducing fuel consumption, minimizing air pollution, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and extending the lifespan of vehicles. It combines environmentally conscious behavior with efficient vehicle operation to achieve sustainable driving that benefits both individuals and the planet. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Key Objectives of Ecodriving: | ||
| + | Reducing Air Pollution: By lowering fuel consumption, ecodriving significantly decreases emissions of harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrocarbons (HC), and particulate matter (PM). This leads to improved air quality and reduced health risks. | ||
| + | Cutting Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Reduced consumption directly translates to lower CO₂ emissions, helping combat climate change. | ||
| + | Optimizing Resource Usage: Smooth driving reduces wear on tires, brakes, and other vehicle components, conserving both materials and energy. | ||
| + | Achieving Financial Savings: Drivers save on fuel costs and vehicle maintenance due to more efficient driving practices. | ||
| + | Enhancing Safety: A smoother, anticipatory driving style decreases the risk of accidents by promoting better control and reaction times. | ||
| + | Core Principles of Ecodriving: | ||
| + | Anticipation and Observation: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Stay aware of traffic flow, predict slowdowns, and avoid unnecessary stops. | ||
| + | Maintain a safe following distance to reduce the need for abrupt braking or acceleration. | ||
| + | Speed Regulation: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Drive at a consistent, moderate speed suited to road conditions. | ||
| + | Avoid rapid accelerations or decelerations, which waste energy and fuel. | ||
| + | Efficient Gear Use: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Shift gears early, keeping the engine in its optimal range (low RPMs). | ||
| + | Use the highest possible gear for cruising without overloading the engine. | ||
| + | Load Reduction: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Remove unnecessary weight and equipment (like roof racks when not in use). | ||
| + | Regularly check and maintain correct tire pressure to improve fuel efficiency. | ||
| + | Minimized Idling and Smart Equipment Use: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Turn off the engine during long stops to prevent unnecessary fuel use. | ||
| + | Limit excessive use of energy-intensive systems like air conditioning or heating, which increase fuel consumption. | ||
| + | Planned Driving Routes: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Opt for routes that minimize stop-and-go traffic and avoid peak hours when feasible. | ||
| + | Combine trips to reduce the total distance traveled. | ||
| + | Broader Benefits of Ecodriving: | ||
| + | Environmental: Reduces air pollution, greenhouse gases, and the overall ecological footprint of driving. | ||
| + | Health: Improved air quality decreases respiratory and cardiovascular risks associated with pollutants. | ||
| + | Economic: Potential savings of up to 20% on fuel and lower maintenance costs. | ||
| + | Comfort: Smoother, less aggressive driving creates a more relaxing driving experience. | ||
| + | Longevity: Prolongs the life of vehicle components, reducing waste and saving resources. | ||
| + | Modern Relevance of Ecodriving: | ||
| + | With growing concerns over air pollution, global warming, and rising energy costs, ecodriving has become a vital component of sustainable mobility. It complements strategies such as transitioning to electric vehicles, increasing the use of public transportation, and adopting alternative fuels. Governments and organizations worldwide are promoting ecodriving through public campaigns, training programs, and incentives to encourage more sustainable driving habits. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In Summary: | ||
| + | Ecodriving is not only about saving fuel—it is a critical step toward reducing air pollution, mitigating climate change, and ensuring a healthier and more sustainable future for all. By integrating ecodriving practices into daily life, drivers can significantly reduce their environmental impact while reaping personal and financial benefits. | ||
| + | Air Pollution Reduction: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Correct: Ecodriving reduces emissions of pollutants like carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrocarbons (HC), and particulate matter (PM). These reductions occur because smoother driving minimizes incomplete combustion, especially during rapid accelerations or idling. | ||
| + | Greenhouse Gas Emissions (CO₂): | ||
| + | |||
| + | Correct: Lower fuel consumption directly reduces carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions since CO₂ is a byproduct of burning fossil fuels. This link is well-established in climate science. | ||
| + | Vehicle Efficiency and Wear: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Correct: Reduced braking, acceleration, and smoother driving reduce mechanical wear on tires, brakes, and the engine, extending vehicle lifespan and conserving materials. | ||
| + | Fuel Savings: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Correct: Ecodriving techniques, such as early gear shifting and consistent speeds, can lower fuel consumption by 10–20%, as documented in energy efficiency studies. | ||
| + | Health and Safety Impacts: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Correct: Reduced air pollution has proven health benefits, including fewer respiratory and cardiovascular issues. Moreover, smoother, anticipatory driving decreases accident risks by enhancing reaction time and control. | ||
| + | Energy Consumption from Accessories: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Correct: Devices like air conditioning can increase fuel consumption by up to 20%, especially at low speeds. This reinforces the recommendation to minimize their use when unnecessary. | ||
| + | Environmental Relevance: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Correct: Ecodriving is an effective strategy to reduce the environmental footprint of traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. While it does not eliminate emissions, it significantly mitigates their impact. | ||
| + | Potential Improvements for Clarity or Emphasis: | ||
| + | Idle Reduction Impact: While cutting the engine during prolonged stops reduces fuel waste, modern vehicles with start-stop systems achieve this automatically, making the practice particularly relevant for older cars. | ||
| + | Electric Vehicles (EVs): Ecodriving principles apply differently to EVs, focusing more on regenerative braking and efficient energy management. Including this distinction could enhance the definition. | ||
| + | Limitations of Ecodriving: It’s important to clarify that ecodriving mitigates, but does not eliminate, emissions and that it is most effective when combined with broader sustainability initiatives like transitioning to cleaner energy sources. | ||
| + | Conclusion: | ||
| + | The definition is scientifically accurate, and no fundamental errors or misunderstandings were found. Including a note on evolving vehicle technologies (e.g., EVs) and emphasizing limitations could further strengthen the comprehensiveness and relevance of the explanation. | ||
| + | Additional Fundamental Concepts to Mention: | ||
| + | Kinetic Energy Management: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ecodriving relies on principles of physics, such as conserving kinetic energy. By reducing unnecessary braking and accelerating, drivers can maintain momentum, which is more fuel-efficient than starting from a complete stop. | ||
| + | Thermal Efficiency of Engines: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Internal combustion engines operate most efficiently within a specific temperature range. Ecodriving practices like steady speeds and avoiding cold starts (by combining trips) help maintain optimal engine temperatures and reduce energy losses. | ||
| + | Aerodynamics: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Excessive speed increases air resistance exponentially, leading to higher fuel consumption. Ecodriving promotes speed moderation to reduce aerodynamic drag and improve fuel efficiency. | ||
| + | Rolling Resistance: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Proper tire inflation minimizes rolling resistance, which directly affects fuel efficiency. Drivers should regularly check tire pressure to optimize vehicle performance and reduce energy waste. | ||
| + | Regenerative Braking (For EVs and Hybrids): | ||
| + | |||
| + | While ecodriving is traditionally associated with internal combustion engine vehicles, it is also relevant for electric and hybrid vehicles. Efficient use of regenerative braking systems in EVs can enhance energy recovery and improve overall efficiency. | ||
| + | Human Behavior and Cognitive Load: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ecodriving requires attentiveness, foresight, and a calm demeanor. Stress, impatience, or aggressive driving counteract the benefits of ecodriving. Training and education can help drivers adopt these habits consistently. | ||
| + | Impact on Urban Air Quality: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ecodriving has a particularly significant impact in urban areas where vehicle density is high. Reducing idling, smooth acceleration, and lower emissions contribute to better air quality, directly benefiting public health. | ||
| + | Fuel Economy Ratings and Real-World Performance: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ecodriving bridges the gap between manufacturers’ fuel economy ratings and real-world vehicle performance. It allows drivers to achieve or exceed the efficiency advertised by automakers. | ||
| + | Behavioral Economics and Incentives: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Behavioral incentives, such as eco-driving rewards or gamified applications, can encourage adoption of these practices. These tools make ecodriving more engaging and measurable for individuals and fleets. | ||
| + | Life Cycle Perspective: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ecodriving reduces the environmental impact of the vehicle during its operational phase. When combined with sustainable manufacturing and end-of-life recycling, it forms part of a holistic approach to reducing a vehicle’s overall environmental footprint. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<!-- ******** Fin Définition Générale ***************************** --> | <!-- ******** Fin Définition Générale ***************************** --> | ||
| Ligne 47 : | Ligne 188 : | ||
|Typologie= <!------------------------------------ Ne pas Modifier --> | |Typologie= <!------------------------------------ Ne pas Modifier --> | ||
<!-- ****************** Commercez les modifications ****************--> | <!-- ****************** Commercez les modifications ****************--> | ||
| − | *.. | + | **Ecodriving: A Holistic Approach to Sustainable Driving** |
| − | + | ||
| − | ... | + | Ecodriving refers to a set of driving techniques and behaviors aimed at reducing fuel consumption, minimizing air pollution, cutting greenhouse gas emissions, and optimizing vehicle performance. Rooted in principles of physics, environmental science, and behavioral efficiency, ecodriving promotes smooth and anticipatory driving to conserve energy, reduce wear on vehicle components, and improve safety. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Key practices include maintaining steady speeds, minimizing unnecessary braking and acceleration, using gears efficiently, and reducing idling. Drivers are encouraged to manage kinetic energy, optimize tire pressure, and avoid excessive loads to maximize efficiency. In urban areas, ecodriving significantly improves air quality by cutting emissions of pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | For electric and hybrid vehicles, ecodriving emphasizes efficient energy management, including maximizing the use of regenerative braking. Beyond individual benefits, ecodriving contributes to broader societal goals by reducing environmental impacts, supporting sustainable urban mobility, and complementing efforts to combat climate change. | |
| + | |||
| + | By integrating technical, environmental, and behavioral principles, ecodriving offers a practical and impactful way for individuals to adopt more responsible and sustainable driving habits. | ||
}}<!-- ******** Fin Fiche Didactique Définition ******************* --> | }}<!-- ******** Fin Fiche Didactique Définition ******************* --> | ||
| Ligne 70 : | Ligne 213 : | ||
Image:Ecodriving_at78.jpg|Ecodriving | Image:Ecodriving_at78.jpg|Ecodriving | ||
Image:Ecodriving_sb78.jpg|New Era is coming | Image:Ecodriving_sb78.jpg|New Era is coming | ||
| − | Image: | + | Image:Ecofriendly-sb78.PNG|ecofriendly leaflet |
| − | Image: | + | Image:Greenhouse-graphic-sb78.jpg|CO2 Effect |
</gallery><!-- ************** Fin modification images***************************--> | </gallery><!-- ************** Fin modification images***************************--> | ||
<!-- ************************* Début modification Vidéo ******************************************************************--> | <!-- ************************* Début modification Vidéo ******************************************************************--> | ||
| Ligne 151 : | Ligne 294 : | ||
<!-- Compléter les pointillés et Supprimer les lignes non utilisées --> | <!-- Compléter les pointillés et Supprimer les lignes non utilisées --> | ||
<!-- ****************** Commercez les modifications *********************** --> | <!-- ****************** Commercez les modifications *********************** --> | ||
| + | |||
| − | *'''[[ | + | *'''[[Individual transport]]''': Ecodriving mainly applies to private car drivers, encouraging behaviors such as smooth acceleration, maintaining a constant speed, and avoiding unnecessary deceleration to save fuel and reduce emissions. |
| − | *'''[[ | + | *'''[[Public transport]]''': Bus drivers and other public transport operators can incorporate ecodriving principles to reduce fuel consumption, minimize mechanical wear, and limit pollutant emissions, thereby improving the sustainability of transport networks. |
| − | *'''[[ | + | *'''[[Freight transport]]''': In logistics and road transport, companies adopt ecodriving to lower operating costs, particularly in long-distance transport, where energy efficiency gains translate into significant savings. |
| − | *'''[[ | + | *'''[[Corporate fleets]]''': Companies with vehicle fleets encourage their employees to practice ecodriving to reduce fuel and maintenance costs while lowering their carbon footprint. |
| − | *'''[[ | + | *'''[[Urban driving]]''': Ecodriving is applied in densely populated urban environments, where anticipating traffic flow and managing frequent stops can reduce fuel consumption and emissions under often inefficient conditions. |
| − | *'''[[ | + | *'''[[Motor sports]]''': Although focused on performance, motorsports can integrate ecodriving principles to improve engine efficiency, particularly in electric or hybrid vehicle competitions. |
| − | *'''[[ | + | *'''[[Driver training and education]]''': Driving schools and awareness campaigns use ecodriving as an educational tool to train new drivers in responsible and environmentally friendly practices. |
| − | *'''[[ | + | *'''[[Development of onboard technologies]]''': Automotive manufacturers integrate tools such as instant fuel consumption indicators, "eco" modes, or energy regeneration systems to help drivers apply ecodriving principles. |
| − | *'''[[ | + | *'''[[Government policies]]''': Governments encourage ecodriving through incentive programs, subsidies for training, or awareness campaigns aimed at achieving national environmental goals. |
| − | *'''[[ | + | *'''[[Air transport]]''': Although less known, ecodriving has an equivalent in aviation, where pilots adopt techniques to optimize fuel consumption, such as flying at an optimal altitude or reducing ground wait times. |
| − | *'''[[ | + | *'''[[Agricultural driving]]''': In agriculture, ecodriving can apply to using machinery such as tractors by optimizing settings and adopting techniques to reduce fuel consumption and operating costs. |
| − | *'''[[ | + | *'''[[Sustainable tourism]]''': As part of responsible tourism, vehicle rental companies or tour guides encourage ecodriving to limit the ecological impact of visitors' travel. |
}}<!--************** Fin Fiche Didactique Explicitations ******************* --> | }}<!--************** Fin Fiche Didactique Explicitations ******************* --> | ||
| + | = {{Widget:Errors-confusions-sheet}} = | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <!-- ****************** Commercez les modifications *************************--> | + | <!-- ************ Début Fiche Didactique Conceptions ******************* --> |
| + | {{Fiche Didactique Conceptions <!----------------------------------------------> | ||
| + | <!-- Spécification des éventuelles Difficultés ou Confusions ou Erreurs ou Conceptions erronées --> | ||
| + | |Difficultés-Confusions-Erreurs-Conceptions= <!--------------------------------> | ||
| + | <!-- Compléter les pointillés et Supprimer les lignes non utilisées------------> | ||
| + | <!-- **************** Commercez les modifications *************************--> | ||
| − | {{@}} | + | {{@}} **Examples of Common Difficulties in Understanding or Interpretation**: |
| − | * | + | * **Confusion Between Ecology and Economy**: Learners might not grasp that eco-driving involves both reducing environmental impact and achieving financial savings. |
| − | * | + | * **Universal Application of Tips**: Assuming all eco-driving tips apply equally to all types of vehicles (electric, hybrid, or internal combustion engines). |
| − | * | + | * **Limited Impact of Individual Behavior**: Underestimating or overestimating the significance of individual driving behavior compared to other factors like vehicle maintenance or road infrastructure. |
| − | * | + | * **Misinterpretation of Performance Indicators**: Difficulty in understanding or interpreting metrics such as average fuel consumption, savings in liters, or CO2 emissions. |
| − | * | + | * **Lack of Practical Connection**: Believing that eco-driving can be limited to theoretical rules without requiring effort in daily driving practice. |
| − | {{@}} | + | {{@}} **Potential Confusions or Misinterpretations**: |
| − | * Confusion | + | * Confusion between **[[Ecology - Economy]]**: The use of the prefix "eco" might lead to focusing on one aspect (ecological or economical) while neglecting the other. |
| − | * Confusion | + | * Confusion between **[[Safe Driving - Eco-Driving]]**: Learners might think that safe driving automatically includes eco-driving principles, though some specific practices differ. |
| − | * Confusion | + | * Confusion between **[[Optimal Speed - Minimum Speed]]**: Believing that saving fuel always means driving slowly, whereas eco-driving recommends a steady, suitable, but not excessive speed. |
| − | * Confusion | + | * Confusion between **[[Immediate Efficiency - Long-Term Efficiency]]**: Thinking that all benefits of eco-driving (like reduced mechanical wear) are noticeable instantly. |
| − | {{@}} | + | {{@}} **Other Frequent Errors**: |
| − | * | + | * Believing eco-driving is unnecessary with modern or electric vehicles, although these vehicles also benefit from optimized driving. |
| − | * | + | * Applying eco-driving techniques without considering terrain or weather conditions, which can reduce effectiveness or increase risks. |
| − | * | + | * Failing to anticipate sufficiently, such as braking suddenly instead of releasing the accelerator when approaching an obstacle or red light. |
| − | * | + | * Confusing instant fuel consumption with average consumption, leading to misinterpretation of performance. |
| − | * | + | * Assuming idling is economical, whereas it wastes fuel unnecessarily. |
| + | * **[[Complexity of Underlying Physical Principles]]**: Explaining concepts like air resistance, inertia, or the impact of speed on fuel consumption might be challenging for those with limited physics knowledge. Simple analogies are crucial. | ||
| + | * **[[Errors About Real Impact]]**: Some might overestimate the environmental effects of eco-driving or underestimate other factors, such as vehicle design or road conditions. | ||
}}<!-- ************** Fin Fiche Didactique Conceptions ********************* --> | }}<!-- ************** Fin Fiche Didactique Conceptions ********************* --> | ||
Version actuelle datée du 27 décembre 2024 à 08:59
 Traduction
Traduction
Écodriving (Français) / Ecodriving (Anglais) / القيادة الاقتصادية (Arabe) / Conducción ecológica (Espagnol) / Condução ecológica (Portugais) / Экодрайвинг (Russe) / Guida ecologica (Italien) / Ökologisches Fahren (Allemand) / 生态驾驶 (Chinois (Mandarin)) / इकोड्राइविंग (Hindi) / エコドライビング (Japonais) / ইকোড্রাইভিং (Bengali).
}}
 Définition
Définition
Domaine, Discipline, Thématique
|Domaine-Discipline-Thématique-1 = Écologie |Domaine-Discipline-Thématique-2 = Physique |Domaine-Discipline-Thématique-3 = Mécanique |Domaine-Discipline-Thématique-4 = Psychologie |Domaine-Discipline-Thématique-5 = Sociologie |Domaine-Discipline-Thématique-6 = Économie |Domaine-Discipline-Thématique-7 = Génie mécanique |Domaine-Discipline-Thématique-8 = Informatique |Domaine-Discipline-Thématique-9 = Ingénierie des transports |Domaine-Discipline-Thématique-10 = Sciences de l’environnement
Définition écrite
Ecodriving: A Responsible and Sustainable Driving Approach
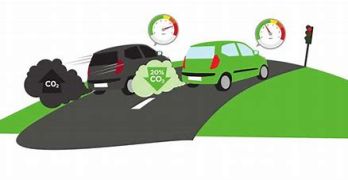
Detailed Definition: Ecodriving, or "eco-driving," refers to a set of driving practices and behaviors aimed at reducing fuel consumption, minimizing greenhouse gas emissions, and extending vehicle lifespan. This approach combines technical and behavioral principles to enable driving that is more environmentally friendly while optimizing costs for the driver.
Main Objectives of Ecodriving: Reducing Pollutant Emissions: Lowering fuel consumption decreases CO₂ emissions, fine particles, and other pollutants harmful to health and the environment. Resource Optimization: Smooth, anticipatory driving reduces wear on tires, brakes, and other vehicle components. Financial Savings: Lower fuel consumption results in direct savings, while reduced wear decreases maintenance costs. Improved Road Safety: Adopting preventive and calmer driving habits reduces the risk of accidents. Core Principles of Ecodriving: Anticipation and Observation:
Observe traffic conditions carefully to foresee slowdowns or stops. Maintain a safe following distance to avoid sudden braking and ensure smooth driving. Speed Management:
Drive at a moderate and consistent speed, suited to traffic conditions. Avoid sudden accelerations and unnecessary braking. Optimal Gear Usage:
Shift to higher gears as soon as possible (typically between 2,000–2,500 RPM for gasoline engines and 1,500–2,000 RPM for diesel engines). Drive in low RPMs when possible without overloading the engine. Reducing Unnecessary Loads:
Remove excess weight from the vehicle (unneeded luggage, unused roof racks, etc.). Ensure tires are properly inflated to the recommended pressure. Strategic Use of Equipment:
Limit excessive use of air conditioning or heating, which increases fuel consumption. Turn off the engine during extended stops (e.g., at traffic lights or in traffic jams). Trip Planning:
Choose the shortest, most fluid routes to minimize stops and starts. Avoid peak traffic hours when possible. Benefits of Ecodriving: Environmental: Significant reduction in pollutant emissions. Economic: Fuel savings of up to 20% depending on driving habits. Comfort: Smoother, more fluid driving reduces stress behind the wheel. Durability: Conservation of resources and reduced long-term ecological impact. Relevance and Modern Context: Given the urgency of the climate crisis and rising energy costs, Ecodriving has become increasingly important. It aligns with broader sustainable mobility efforts, complementing initiatives such as electric vehicle adoption and the promotion of public transport. Many governments and organizations actively promote Ecodriving through awareness campaigns, specialized training, and financial incentives. Ecodriving: A Comprehensive Definition of Responsible and Sustainable Driving
Definition: Ecodriving, or "eco-driving," encompasses a set of techniques and habits aimed at reducing fuel consumption, minimizing air pollution, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and extending the lifespan of vehicles. It combines environmentally conscious behavior with efficient vehicle operation to achieve sustainable driving that benefits both individuals and the planet.
Key Objectives of Ecodriving: Reducing Air Pollution: By lowering fuel consumption, ecodriving significantly decreases emissions of harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrocarbons (HC), and particulate matter (PM). This leads to improved air quality and reduced health risks. Cutting Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Reduced consumption directly translates to lower CO₂ emissions, helping combat climate change. Optimizing Resource Usage: Smooth driving reduces wear on tires, brakes, and other vehicle components, conserving both materials and energy. Achieving Financial Savings: Drivers save on fuel costs and vehicle maintenance due to more efficient driving practices. Enhancing Safety: A smoother, anticipatory driving style decreases the risk of accidents by promoting better control and reaction times. Core Principles of Ecodriving: Anticipation and Observation:
Stay aware of traffic flow, predict slowdowns, and avoid unnecessary stops. Maintain a safe following distance to reduce the need for abrupt braking or acceleration. Speed Regulation:
Drive at a consistent, moderate speed suited to road conditions. Avoid rapid accelerations or decelerations, which waste energy and fuel. Efficient Gear Use:
Shift gears early, keeping the engine in its optimal range (low RPMs). Use the highest possible gear for cruising without overloading the engine. Load Reduction:
Remove unnecessary weight and equipment (like roof racks when not in use). Regularly check and maintain correct tire pressure to improve fuel efficiency. Minimized Idling and Smart Equipment Use:
Turn off the engine during long stops to prevent unnecessary fuel use. Limit excessive use of energy-intensive systems like air conditioning or heating, which increase fuel consumption. Planned Driving Routes:
Opt for routes that minimize stop-and-go traffic and avoid peak hours when feasible. Combine trips to reduce the total distance traveled. Broader Benefits of Ecodriving: Environmental: Reduces air pollution, greenhouse gases, and the overall ecological footprint of driving. Health: Improved air quality decreases respiratory and cardiovascular risks associated with pollutants. Economic: Potential savings of up to 20% on fuel and lower maintenance costs. Comfort: Smoother, less aggressive driving creates a more relaxing driving experience. Longevity: Prolongs the life of vehicle components, reducing waste and saving resources. Modern Relevance of Ecodriving: With growing concerns over air pollution, global warming, and rising energy costs, ecodriving has become a vital component of sustainable mobility. It complements strategies such as transitioning to electric vehicles, increasing the use of public transportation, and adopting alternative fuels. Governments and organizations worldwide are promoting ecodriving through public campaigns, training programs, and incentives to encourage more sustainable driving habits.
In Summary: Ecodriving is not only about saving fuel—it is a critical step toward reducing air pollution, mitigating climate change, and ensuring a healthier and more sustainable future for all. By integrating ecodriving practices into daily life, drivers can significantly reduce their environmental impact while reaping personal and financial benefits. Air Pollution Reduction:
Correct: Ecodriving reduces emissions of pollutants like carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrocarbons (HC), and particulate matter (PM). These reductions occur because smoother driving minimizes incomplete combustion, especially during rapid accelerations or idling. Greenhouse Gas Emissions (CO₂):
Correct: Lower fuel consumption directly reduces carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions since CO₂ is a byproduct of burning fossil fuels. This link is well-established in climate science. Vehicle Efficiency and Wear:
Correct: Reduced braking, acceleration, and smoother driving reduce mechanical wear on tires, brakes, and the engine, extending vehicle lifespan and conserving materials. Fuel Savings:
Correct: Ecodriving techniques, such as early gear shifting and consistent speeds, can lower fuel consumption by 10–20%, as documented in energy efficiency studies. Health and Safety Impacts:
Correct: Reduced air pollution has proven health benefits, including fewer respiratory and cardiovascular issues. Moreover, smoother, anticipatory driving decreases accident risks by enhancing reaction time and control. Energy Consumption from Accessories:
Correct: Devices like air conditioning can increase fuel consumption by up to 20%, especially at low speeds. This reinforces the recommendation to minimize their use when unnecessary. Environmental Relevance:
Correct: Ecodriving is an effective strategy to reduce the environmental footprint of traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. While it does not eliminate emissions, it significantly mitigates their impact. Potential Improvements for Clarity or Emphasis: Idle Reduction Impact: While cutting the engine during prolonged stops reduces fuel waste, modern vehicles with start-stop systems achieve this automatically, making the practice particularly relevant for older cars. Electric Vehicles (EVs): Ecodriving principles apply differently to EVs, focusing more on regenerative braking and efficient energy management. Including this distinction could enhance the definition. Limitations of Ecodriving: It’s important to clarify that ecodriving mitigates, but does not eliminate, emissions and that it is most effective when combined with broader sustainability initiatives like transitioning to cleaner energy sources. Conclusion: The definition is scientifically accurate, and no fundamental errors or misunderstandings were found. Including a note on evolving vehicle technologies (e.g., EVs) and emphasizing limitations could further strengthen the comprehensiveness and relevance of the explanation. Additional Fundamental Concepts to Mention: Kinetic Energy Management:
Ecodriving relies on principles of physics, such as conserving kinetic energy. By reducing unnecessary braking and accelerating, drivers can maintain momentum, which is more fuel-efficient than starting from a complete stop. Thermal Efficiency of Engines:
Internal combustion engines operate most efficiently within a specific temperature range. Ecodriving practices like steady speeds and avoiding cold starts (by combining trips) help maintain optimal engine temperatures and reduce energy losses. Aerodynamics:
Excessive speed increases air resistance exponentially, leading to higher fuel consumption. Ecodriving promotes speed moderation to reduce aerodynamic drag and improve fuel efficiency. Rolling Resistance:
Proper tire inflation minimizes rolling resistance, which directly affects fuel efficiency. Drivers should regularly check tire pressure to optimize vehicle performance and reduce energy waste. Regenerative Braking (For EVs and Hybrids):
While ecodriving is traditionally associated with internal combustion engine vehicles, it is also relevant for electric and hybrid vehicles. Efficient use of regenerative braking systems in EVs can enhance energy recovery and improve overall efficiency. Human Behavior and Cognitive Load:
Ecodriving requires attentiveness, foresight, and a calm demeanor. Stress, impatience, or aggressive driving counteract the benefits of ecodriving. Training and education can help drivers adopt these habits consistently. Impact on Urban Air Quality:
Ecodriving has a particularly significant impact in urban areas where vehicle density is high. Reducing idling, smooth acceleration, and lower emissions contribute to better air quality, directly benefiting public health. Fuel Economy Ratings and Real-World Performance:
Ecodriving bridges the gap between manufacturers’ fuel economy ratings and real-world vehicle performance. It allows drivers to achieve or exceed the efficiency advertised by automakers. Behavioral Economics and Incentives:
Behavioral incentives, such as eco-driving rewards or gamified applications, can encourage adoption of these practices. These tools make ecodriving more engaging and measurable for individuals and fleets. Life Cycle Perspective:
Ecodriving reduces the environmental impact of the vehicle during its operational phase. When combined with sustainable manufacturing and end-of-life recycling, it forms part of a holistic approach to reducing a vehicle’s overall environmental footprint.
Ecodriving refers to a set of driving techniques and behaviors aimed at reducing fuel consumption, minimizing air pollution, cutting greenhouse gas emissions, and optimizing vehicle performance. Rooted in principles of physics, environmental science, and behavioral efficiency, ecodriving promotes smooth and anticipatory driving to conserve energy, reduce wear on vehicle components, and improve safety. Key practices include maintaining steady speeds, minimizing unnecessary braking and acceleration, using gears efficiently, and reducing idling. Drivers are encouraged to manage kinetic energy, optimize tire pressure, and avoid excessive loads to maximize efficiency. In urban areas, ecodriving significantly improves air quality by cutting emissions of pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. For electric and hybrid vehicles, ecodriving emphasizes efficient energy management, including maximizing the use of regenerative braking. Beyond individual benefits, ecodriving contributes to broader societal goals by reducing environmental impacts, supporting sustainable urban mobility, and complementing efforts to combat climate change. By integrating technical, environmental, and behavioral principles, ecodriving offers a practical and impactful way for individuals to adopt more responsible and sustainable driving habits. |
Définition graphique
- AUTRES MEDIAS
![]() Ecodriving (Discipline)
Ecodriving (Discipline)
![]() Ecodriving: (Discipline)
Ecodriving: (Discipline)
![]() Ecodriving: (Discipline)
Ecodriving: (Discipline)
![]() Ecodriving: (Discipline)
Ecodriving: (Discipline)
![]() Ecodriving: (Discipline)
Ecodriving: (Discipline)
![]() Ecodriving
Ecodriving
![]() Ecodriving
Ecodriving
![]() Représentation graphique spatiale Ecodriving: carte conceptuelle (cmap)
Représentation graphique spatiale Ecodriving: carte conceptuelle (cmap)
![]() Document PDF Ecodriving: Document PDF
Document PDF Ecodriving: Document PDF
![]() Image/Figure Ecodriving: Titre de l'image ou de la figure
Image/Figure Ecodriving: Titre de l'image ou de la figure
 Concepts ou notions associés
Concepts ou notions associés
Énergie / Consommation / Rendement / Aérodynamique / Friction / Inertie / Émissions / Pollution / Accélération / Freinage / Vitesse / Trajectoire / Éco-conduite / Durabilité / Environnement / Optimisation / Propulsion / Maintenance / Technologie / Résistance / Thermodynamique / Planification / Transport / Sécurité / Habitabilité /
 Exemples, applications, utilisations
Exemples, applications, utilisations
|
Widget:Errors-confusions-sheet
![]() **Examples of Common Difficulties in Understanding or Interpretation**:
**Examples of Common Difficulties in Understanding or Interpretation**:
- **Confusion Between Ecology and Economy**: Learners might not grasp that eco-driving involves both reducing environmental impact and achieving financial savings.
- **Universal Application of Tips**: Assuming all eco-driving tips apply equally to all types of vehicles (electric, hybrid, or internal combustion engines).
- **Limited Impact of Individual Behavior**: Underestimating or overestimating the significance of individual driving behavior compared to other factors like vehicle maintenance or road infrastructure.
- **Misinterpretation of Performance Indicators**: Difficulty in understanding or interpreting metrics such as average fuel consumption, savings in liters, or CO2 emissions.
- **Lack of Practical Connection**: Believing that eco-driving can be limited to theoretical rules without requiring effort in daily driving practice.
![]() **Potential Confusions or Misinterpretations**:
**Potential Confusions or Misinterpretations**:
- Confusion between **Ecology - Economy**: The use of the prefix "eco" might lead to focusing on one aspect (ecological or economical) while neglecting the other.
- Confusion between **Safe Driving - Eco-Driving**: Learners might think that safe driving automatically includes eco-driving principles, though some specific practices differ.
- Confusion between **Optimal Speed - Minimum Speed**: Believing that saving fuel always means driving slowly, whereas eco-driving recommends a steady, suitable, but not excessive speed.
- Confusion between **Immediate Efficiency - Long-Term Efficiency**: Thinking that all benefits of eco-driving (like reduced mechanical wear) are noticeable instantly.
- Believing eco-driving is unnecessary with modern or electric vehicles, although these vehicles also benefit from optimized driving.
- Applying eco-driving techniques without considering terrain or weather conditions, which can reduce effectiveness or increase risks.
- Failing to anticipate sufficiently, such as braking suddenly instead of releasing the accelerator when approaching an obstacle or red light.
- Confusing instant fuel consumption with average consumption, leading to misinterpretation of performance.
- Assuming idling is economical, whereas it wastes fuel unnecessarily.
- **Complexity of Underlying Physical Principles**: Explaining concepts like air resistance, inertia, or the impact of speed on fuel consumption might be challenging for those with limited physics knowledge. Simple analogies are crucial.
- **Errors About Real Impact**: Some might overestimate the environmental effects of eco-driving or underestimate other factors, such as vehicle design or road conditions.
 Questions possibles
Questions possibles
 Liaisons enseignements et programmes
Liaisons enseignements et programmes
Idées ou Réflexions liées à son enseignement
Education: Autres liens, sites ou portails
 Bibliographie
Bibliographie
Pour citer cette page: ([1])
ABROUGUI, M & al, 2024. Ecodriving. In Didaquest [en ligne]. <http:www.didaquest.org/wiki/Ecodriving>, consulté le 27, décembre, 2024
- ..................
- ..................
- ..................
- ..................
- Pages utilisant des arguments dupliqués dans les appels de modèle
- Sponsors Education
- Énergie
- Consommation
- Rendement
- Aérodynamique
- Friction
- Inertie
- Émissions
- Pollution
- Accélération
- Freinage
- Vitesse
- Trajectoire
- Éco-conduite
- Durabilité
- Environnement
- Optimisation
- Propulsion
- Maintenance
- Technologie
- Résistance
- Thermodynamique
- Planification
- Transport
- Sécurité
- Habitabilité
- Concepts
- Ecodriving
- Ecodriving (Concepts)
- Fiche conceptuelle didactique