Différences entre versions de « Nouns »
| Ligne 253 : | Ligne 253 : | ||
<!-- ************ Commercez les modifications *********************--> | <!-- ************ Commercez les modifications *********************--> | ||
| − | * [[ | + | *'''[[What is the difference between common nouns and proper nouns?]]''': |
| − | + | Common nouns refer to general categories or types (e.g., "city"), while proper nouns name specific entities (e.g., "New York") and are always capitalized. | |
| − | |||
| + | *'''[[How can you tell the difference between countable and uncountable nouns?]]''': | ||
| + | Countable nouns can be pluralized and used with numbers (e.g., "three apples"), while uncountable nouns represent mass or abstract concepts that cannot be counted directly (e.g., "water"). | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''[[Why is “information” uncountable, but “fact” is countable?]]''': | ||
| + | "Information" refers to a mass or collection of knowledge, while "fact" represents individual, countable pieces of knowledge. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''[[What are abstract nouns, and how do they differ from concrete nouns?]]''': | ||
| + | Abstract nouns refer to ideas, qualities, or states that cannot be perceived with the senses (e.g., "happiness"). Concrete nouns represent things you can see, touch, or feel (e.g., "book"). | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''[[How do you form the plural of irregular nouns?]]''': | ||
| + | Irregular nouns don’t follow standard pluralization rules. For example: "child" → "children," "mouse" → "mice." These must be memorized. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''[[How do you differentiate between a possessive noun and a contraction?]]''': | ||
| + | A possessive noun shows ownership (e.g., "the dog’s tail"), while a contraction combines words (e.g., "it’s" = "it is"). | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''[[When should you capitalize nouns?]]''': | ||
| + | Capitalize proper nouns (e.g., "Paris") and nouns in titles. Do not capitalize common nouns unless they begin a sentence. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''[[What is a collective noun, and is it singular or plural?]]''': | ||
| + | A collective noun (e.g., "team") refers to a group. It is singular in American English ("The team is winning") but can be plural in British English ("The team are winning"). | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''[[What are compound nouns, and how do you pluralize them?]]''': | ||
| + | Compound nouns combine two or more words to form a single idea (e.g., "mother-in-law"). Pluralize the most important word: "mothers-in-law." | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''[[How do gerunds differ from other nouns?]]''': | ||
| + | Gerunds are verbs ending in -ing that function as nouns (e.g., "Swimming is fun"). They describe actions or activities rather than things. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''[[What are gendered nouns, and why can they be confusing?]]''': | ||
| + | Gendered nouns assign gender to objects or roles (e.g., "actor" vs. "actress"). This can be confusing in contexts advocating for gender-neutral language. | ||
}}<!-- ******** Fin Fiche Didactique Questions ******************* --> | }}<!-- ******** Fin Fiche Didactique Questions ******************* --> | ||
Version du 11 décembre 2024 à 18:32
 Traduction
Traduction
Noms (Français) / Nouns (Anglais) / أسماء (Arabe) / Sustantivos (Espagnol) / Substantivos (Portugais) / Существительные (Russe) / Sostantivi (Italien) / Nomen (Allemand) / 名词 (Chinois (Mandarin)) / संज्ञा (Hindi) / 名詞 (Japonais) / বিশেষ্য (Bengali)
 Définition
Définition
Domaine, Discipline, Thématique
Définition écrite
![]() Basic Definition
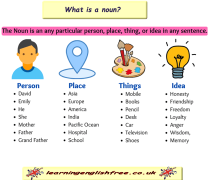
A noun is a word that designates a person, place, object, or idea.
Basic Definition
A noun is a word that designates a person, place, object, or idea.
![]() Intermediate Definition
A noun is a grammatical category that serves to identify and designate concrete or abstract entities. It can be classified into different subcategories, such as proper nouns, which refer to unique individuals, and common nouns, which refer to classes of objects or ideas.
Intermediate Definition
A noun is a grammatical category that serves to identify and designate concrete or abstract entities. It can be classified into different subcategories, such as proper nouns, which refer to unique individuals, and common nouns, which refer to classes of objects or ideas.
![]() Advanced Definition
The noun, as a fundamental element of language, plays a crucial role in structuring discourse. It can be analyzed across several dimensions: syntactically, where it often functions as the subject or object in a sentence; semantically, where it conveys specific meanings; and pragmatically, where its usage varies according to social and cultural context. Nouns may also be affected by morphological properties such as gender and number.
Advanced Definition
The noun, as a fundamental element of language, plays a crucial role in structuring discourse. It can be analyzed across several dimensions: syntactically, where it often functions as the subject or object in a sentence; semantically, where it conveys specific meanings; and pragmatically, where its usage varies according to social and cultural context. Nouns may also be affected by morphological properties such as gender and number.
![]() In-Depth Definition
A noun is an essential lexical unit within linguistic systems that serves to reference both concrete and abstract entities. Syntactically, it can function as a subject, direct or indirect object, and complement. Semantically, nouns are divided into categories such as proper nouns (which denote specific individuals or locations) and common nouns (which encompass classes of objects or ideas). Morphologically, they are subject to variations in gender (masculine or feminine) and number (singular or plural), influencing their agreement with other elements in the sentence. Furthermore, from a pragmatic perspective, the use of nouns is contextually determined and can vary according to social and cultural conventions. This complexity underscores the importance of nouns in constructing meaning and facilitating human communication.
}}
In-Depth Definition
A noun is an essential lexical unit within linguistic systems that serves to reference both concrete and abstract entities. Syntactically, it can function as a subject, direct or indirect object, and complement. Semantically, nouns are divided into categories such as proper nouns (which denote specific individuals or locations) and common nouns (which encompass classes of objects or ideas). Morphologically, they are subject to variations in gender (masculine or feminine) and number (singular or plural), influencing their agreement with other elements in the sentence. Furthermore, from a pragmatic perspective, the use of nouns is contextually determined and can vary according to social and cultural conventions. This complexity underscores the importance of nouns in constructing meaning and facilitating human communication.
}}
Définition graphique
- AUTRES MEDIAS
![]() Nouns (Discipline)
Nouns (Discipline)
![]() Nouns: (Discipline)
Nouns: (Discipline)
![]() Nouns: (Discipline)
Nouns: (Discipline)
![]() Nouns: (Discipline)
Nouns: (Discipline)
![]() Nouns: (Discipline)
Nouns: (Discipline)
![]() Nouns
Nouns
![]() Nouns
Nouns
![]() : carte conceptuelle (cmap)
: carte conceptuelle (cmap)
![]() Document PDF Nouns: Document PDF
Document PDF Nouns: Document PDF
![]() Image/Figure Nouns: Titre de l'image ou de la figure
Image/Figure Nouns: Titre de l'image ou de la figure
 Concepts ou notions associés
Concepts ou notions associés
Noun Phrase / Proper Nouns / Common Nouns / Collective Nouns / Abstract Nouns / Concrete Nouns / Countable Nouns / Uncountable Nouns / Gender in Nouns / Number Agreement / Case in Nouns / Noun Functions / Syntax of Nouns / Morphology of Nouns / Semantic Roles of Nouns / Noun Modifiers / Determiners with Nouns / Possessive Nouns / Noun Clauses / Compounding in Nouns / Derivation of Nouns / Inflection of Nouns / Nominalization / Language Acquisition of Nouns / Pragmatics of Noun Usage /
 Exemples, applications, utilisations
Exemples, applications, utilisations
................................................................................ ................................................................................ ................................................................................
................................................................................ ................................................................................ ................................................................................ |
 Erreurs ou confusions éventuelles
Erreurs ou confusions éventuelles
![]() Exemples de difficultés de compréhension ou d'interprétation courantes:
Exemples de difficultés de compréhension ou d'interprétation courantes:
Students may struggle to differentiate between common nouns (e.g., "city") and proper nouns (e.g., "Paris"). This often leads to errors in capitalization, as they might capitalize common nouns unnecessarily or fail to capitalize proper nouns.
Students may find it challenging to understand the difference between abstract nouns (e.g., "happiness") and concrete nouns (e.g., "table"). This confusion can arise because abstract nouns are intangible and harder to visualize, making them less intuitive to grasp.
Some students might not realize that certain nouns are inherently uncountable (e.g., "water," "information"), leading them to make errors such as saying "informations" or "three waters." Additionally, understanding when an uncountable noun can take a plural form in specific contexts (e.g., "waters" meaning multiple bodies of water) can add to the confusion.
The irregular plural forms of some nouns (e.g., "child" → "children," "tooth" → "teeth") can be difficult for students to memorize and apply correctly. They may overgeneralize regular pluralization rules, resulting in errors like "childs" or "tooths."
Students may have difficulty forming possessive nouns, especially when dealing with plural nouns (e.g., "dogs' tails" vs. "dog's tail"). They might also confuse possessive forms with contractions, such as mixing up "it's" and "its."
Nouns that can also function as verbs or adjectives (e.g., "run," "light") may confuse students when interpreting or constructing sentences. For instance, they might misidentify "run" as a verb in "a morning run."
For students learning nouns in languages that assign grammatical gender (e.g., French, Spanish), identifying and remembering the gender of each noun can be particularly challenging. Errors in noun-adjective agreement or article selection frequently occur as a result.
![]() Confusions ou glissement de sens potentiels
Confusions ou glissement de sens potentiels
Students often mix up common and proper nouns. For instance, they might capitalize "school" or "river" unnecessarily or fail to capitalize names like "Amazon River." This confusion stems from a lack of clarity about when a noun refers to a specific entity versus a general category.
The distinction between countable and uncountable nouns can be confusing, particularly when a noun can function as both, depending on context (e.g., "coffee" as an uncountable substance vs. "two coffees" referring to servings). Students may also mistakenly apply pluralization rules universally, leading to errors like "furnitures" or "advices."
Students may confuse abstract nouns with concrete ones when abstract concepts are expressed metaphorically or visually. For example, in "The foundation of trust is strong," they might misinterpret "foundation" as a physical object rather than an abstract idea.
The difference between possessive forms and contractions is a frequent source of confusion. For example, students might write "The dog wagged it's tail" instead of "its tail," misinterpreting "it's" as a possessive rather than a contraction of "it is."
Irregular plural forms (e.g., "children" or "mice") may lead to errors when students assume they are singular. Similarly, singular nouns that look plural (e.g., "news," "physics") might cause confusion, with students attempting to pluralize them incorrectly or treat them as plural in verbs (e.g., "The news are interesting").
Students often struggle with gerunds that function as nouns but resemble verbs (e.g., "Swimming is fun"). They might misidentify "swimming" as a verb in this context, causing confusion in sentence construction or analysis.
In languages with gendered nouns (e.g., French or Spanish), students may struggle to reconcile traditional grammatical rules with modern gender-neutral language usage, especially for professions or roles (e.g., "le professeur" as masculine in French vs. neutral intentions).
![]() Autres erreurs fréquentes:
Autres erreurs fréquentes:
Students may confuse nouns with adjectives, especially in sentences where an adjective precedes a noun (e.g., "beautiful garden"). They might mistakenly identify "beautiful" as a noun instead of recognizing it as a descriptor for the noun "garden."
Some words can function as both nouns and verbs depending on the context (e.g., "run" in "I went for a run" vs. "I run every day"). This ambiguity can lead to errors in identifying grammatical functions.
Collective nouns like "team" or "family" are sometimes misinterpreted as plural nouns, leading to errors in subject-verb agreement. For instance, a student might write "The team are winning" instead of "The team is winning."
Students might struggle to pair nouns with the correct articles. For example, they might say "a information" instead of "an item of information" or omit the article entirely when it’s required for proper usage.
Some nouns require specific prepositions (e.g., "interested in," "dependence on"). Students might make mistakes like saying "interested for music" instead of "interested in music."
Compound nouns (e.g., "toothbrush" or "mother-in-law") are sometimes misinterpreted. Students might separate them into two words or reverse their order, leading to mistakes like "tooth brush" or "law-mother-in."
Students may struggle with how to pluralize compound nouns, for instance, writing "brother-in-laws" instead of "brothers-in-law," resulting in grammatical errors.
For language learners, some nouns lack a direct equivalent in their native language, or their usage differs. For example, in French, "pain" and "bread" can overlap in certain contexts, which may lead to awkward translations or conceptual errors.
Students may struggle to use abstract nouns correctly with determiners. For instance, they might say "the happiness" instead of simply "happiness" in sentences like "Happiness is important."
 Questions possibles
Questions possibles
Common nouns refer to general categories or types (e.g., "city"), while proper nouns name specific entities (e.g., "New York") and are always capitalized.
Countable nouns can be pluralized and used with numbers (e.g., "three apples"), while uncountable nouns represent mass or abstract concepts that cannot be counted directly (e.g., "water").
"Information" refers to a mass or collection of knowledge, while "fact" represents individual, countable pieces of knowledge.
Abstract nouns refer to ideas, qualities, or states that cannot be perceived with the senses (e.g., "happiness"). Concrete nouns represent things you can see, touch, or feel (e.g., "book").
Irregular nouns don’t follow standard pluralization rules. For example: "child" → "children," "mouse" → "mice." These must be memorized.
A possessive noun shows ownership (e.g., "the dog’s tail"), while a contraction combines words (e.g., "it’s" = "it is").
Capitalize proper nouns (e.g., "Paris") and nouns in titles. Do not capitalize common nouns unless they begin a sentence.
A collective noun (e.g., "team") refers to a group. It is singular in American English ("The team is winning") but can be plural in British English ("The team are winning").
Compound nouns combine two or more words to form a single idea (e.g., "mother-in-law"). Pluralize the most important word: "mothers-in-law."
Gerunds are verbs ending in -ing that function as nouns (e.g., "Swimming is fun"). They describe actions or activities rather than things.
Gendered nouns assign gender to objects or roles (e.g., "actor" vs. "actress"). This can be confusing in contexts advocating for gender-neutral language.
 Liaisons enseignements et programmes
Liaisons enseignements et programmes
Idées ou Réflexions liées à son enseignement
Education: Autres liens, sites ou portails
 Bibliographie
Bibliographie
Pour citer cette page: ([1])
ABROUGUI, M & al, 2024. Nouns. In Didaquest [en ligne]. <http:www.didaquest.org/wiki/Nouns>, consulté le 22, décembre, 2024
- ..................
- ..................
- ..................
- ..................
- Pages utilisant des arguments dupliqués dans les appels de modèle
- Sponsors Education
- Linguistics (Concepts)
- Psycholinguistics (Concepts)
- Morphology (Concepts)
- Syntax (Concepts)
- Semantics (Concepts)
- Pragmatics (Concepts)
- Lexicology (Concepts)
- Sociolinguistics (Concepts)
- Computational Linguistics (Concepts)
- Semiotics (Concepts)
- Noun Phrase
- Proper Nouns
- Common Nouns
- Collective Nouns
- Abstract Nouns
- Concrete Nouns
- Countable Nouns
- Uncountable Nouns
- Gender in Nouns
- Number Agreement
- Case in Nouns
- Noun Functions
- Syntax of Nouns
- Morphology of Nouns
- Semantic Roles of Nouns
- Noun Modifiers
- Determiners with Nouns
- Possessive Nouns
- Noun Clauses
- Compounding in Nouns
- Derivation of Nouns
- Inflection of Nouns
- Nominalization
- Language Acquisition of Nouns
- Pragmatics of Noun Usage
- Concepts
- Nouns
- Nouns (Concepts)
- Fiche conceptuelle didactique